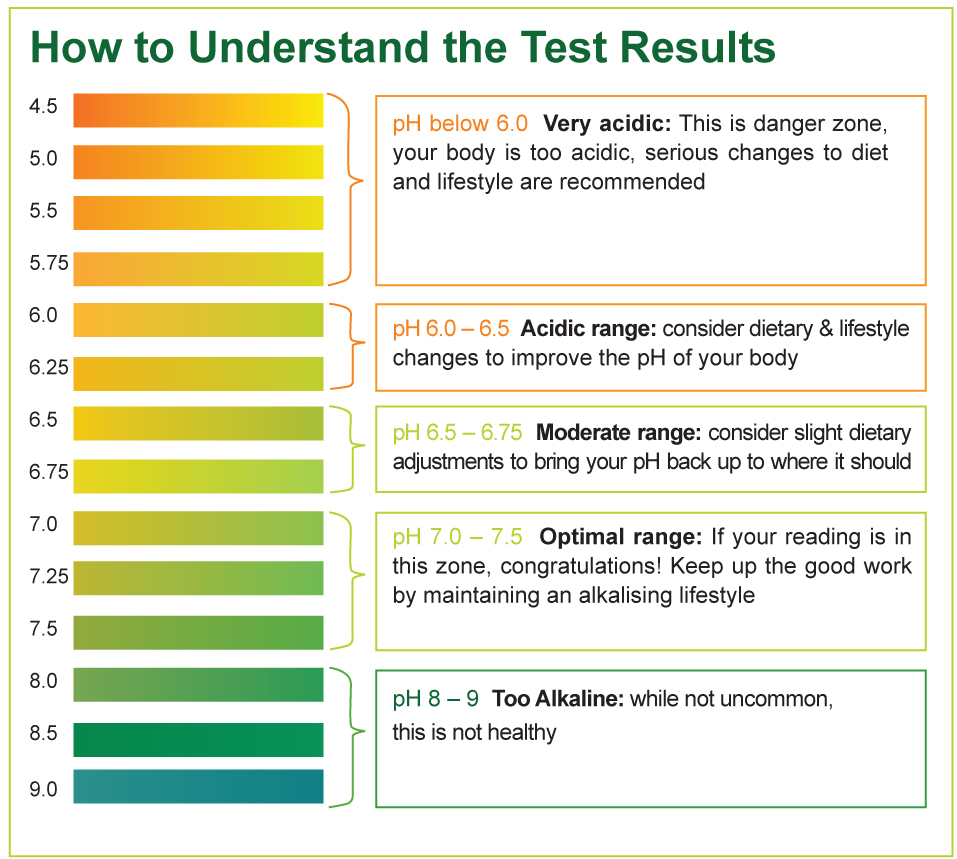
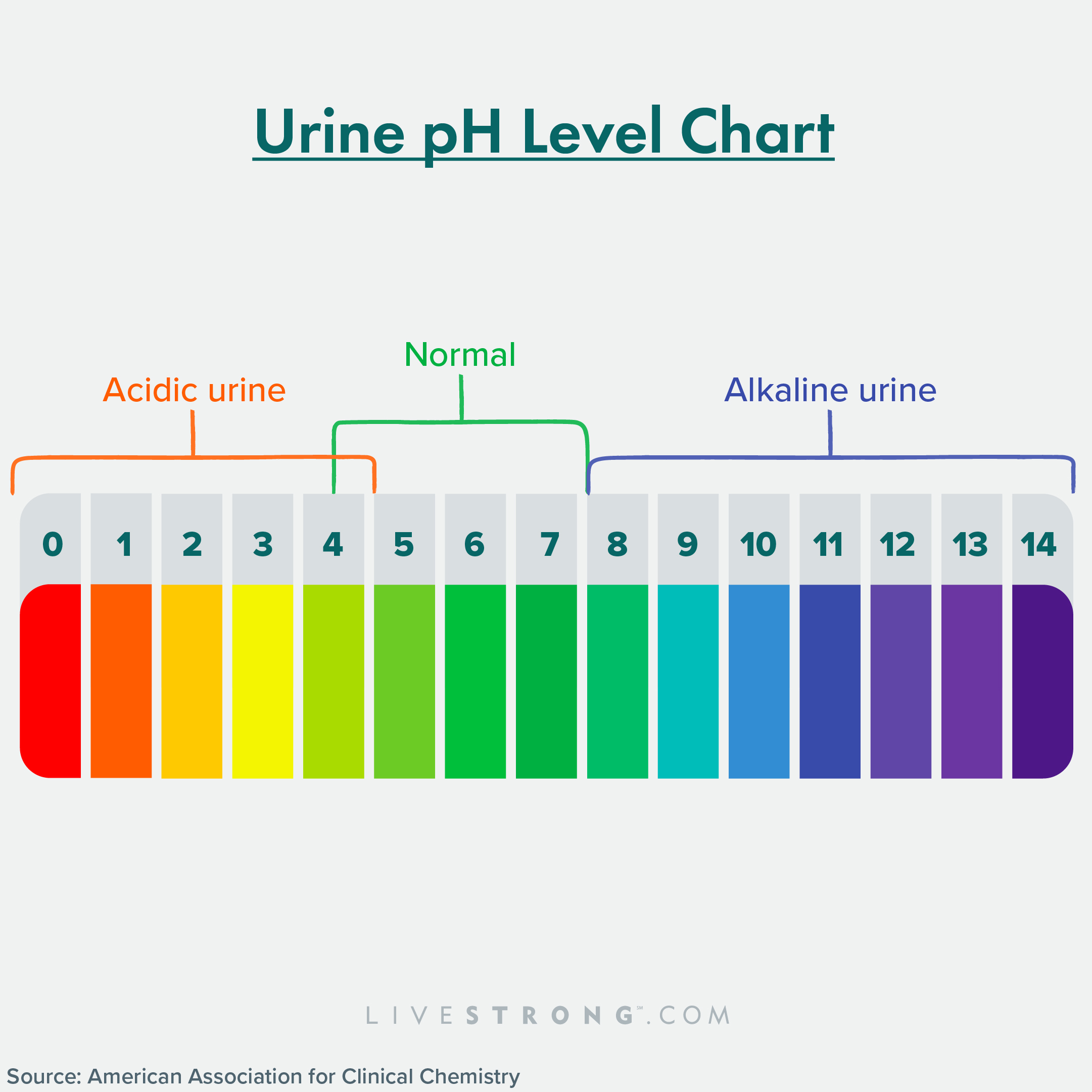
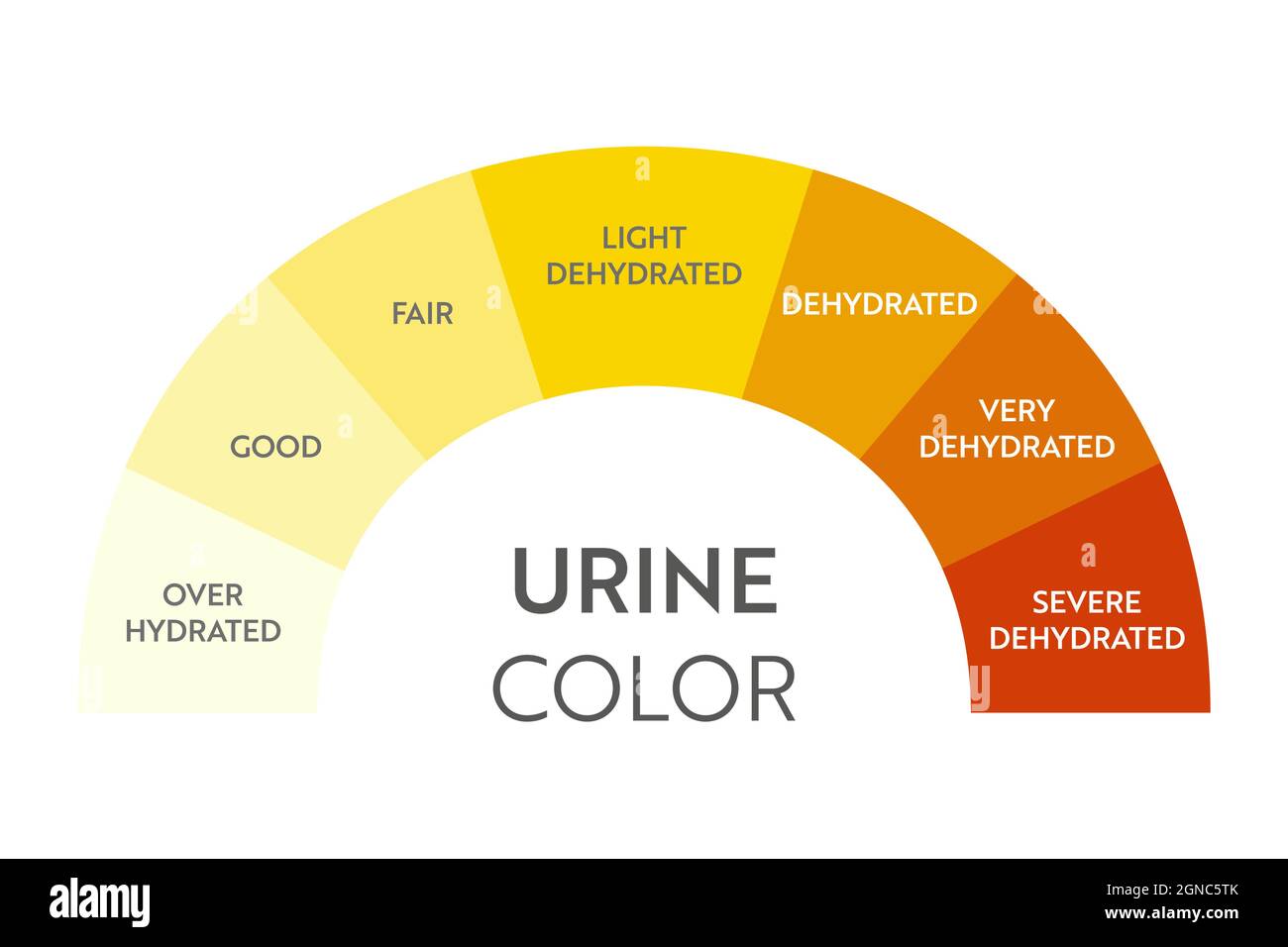
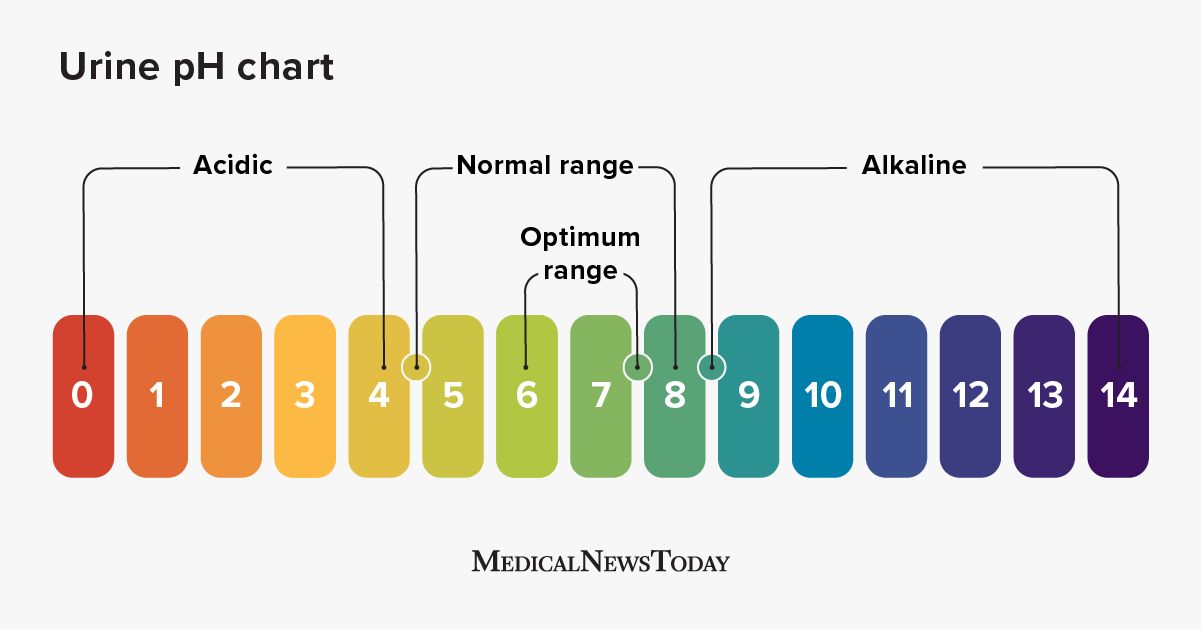
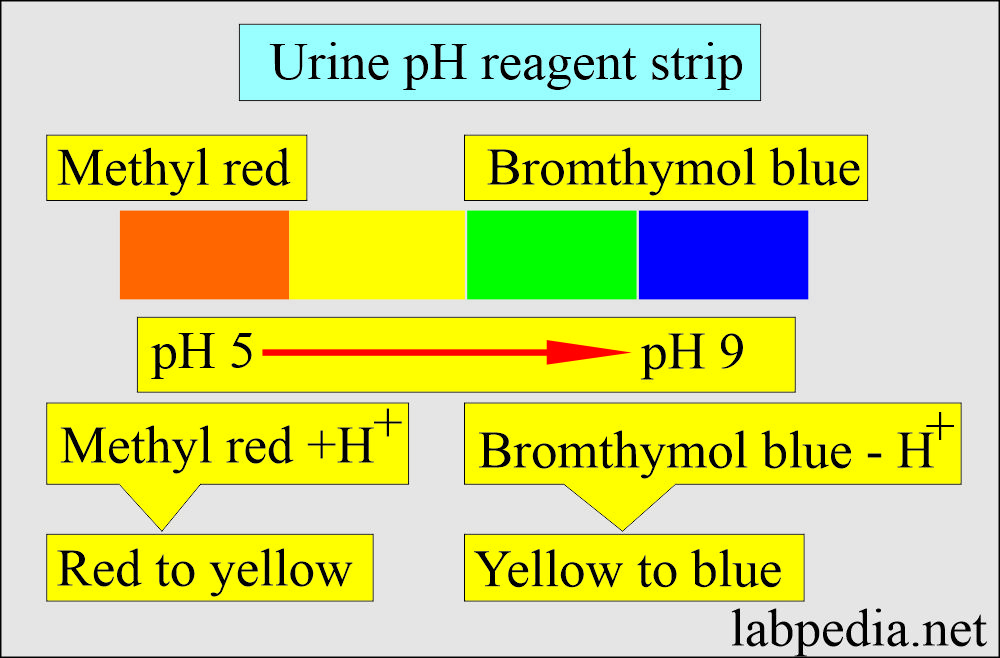
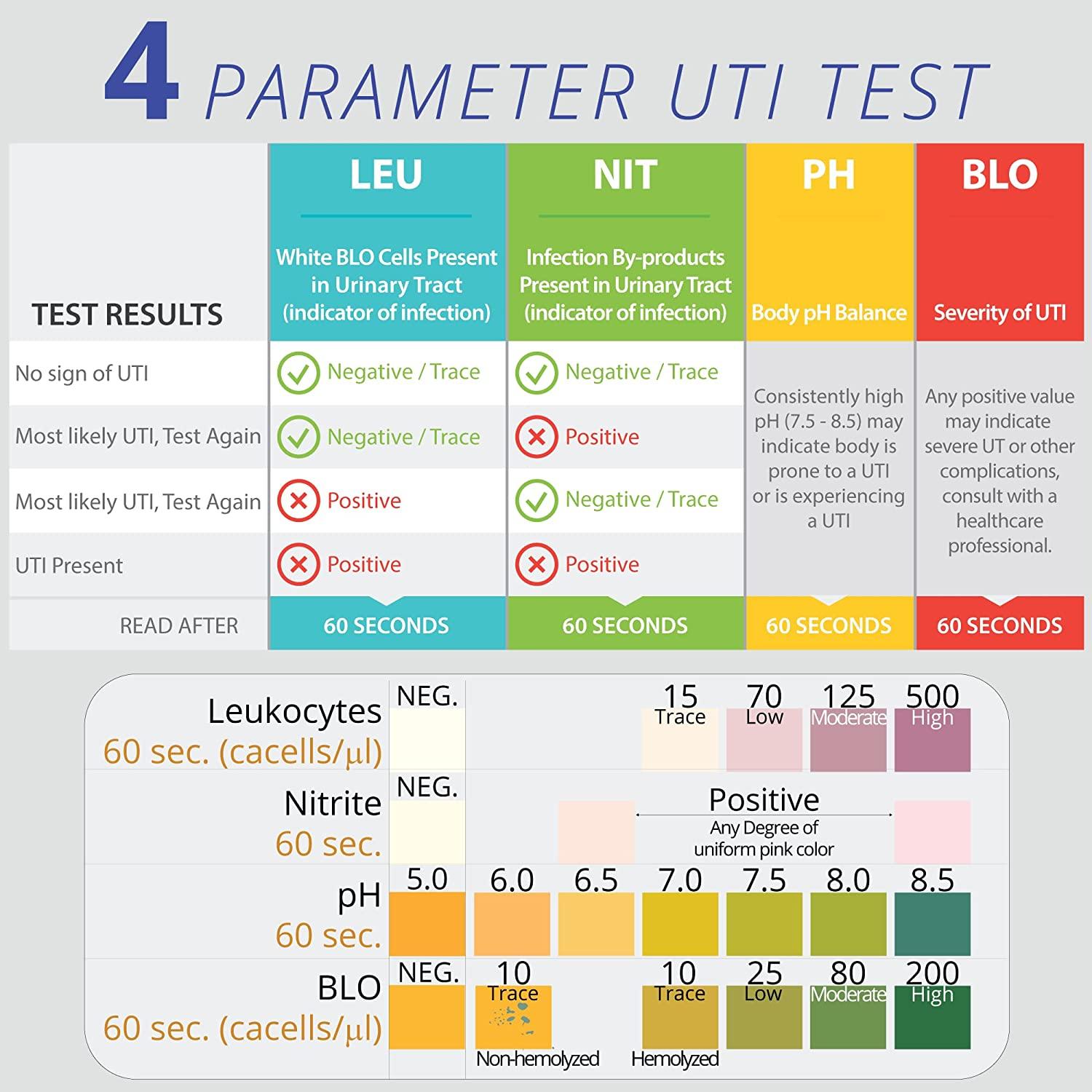
Urine Ph Level Chart
Urine Ph Level Chart - Urine, liquid or semisolid solution of metabolic wastes and certain other, often toxic, substances that the excretory organs withdraw from the circulatory fluids and expel from the. Your blood carries it to the kidneys. The color, odor, density, and frequency of your urine can tell you a lot about your health, as can the presence of proteins and ketones. Some urine color changes may be a sign of an infection or a problem with the liver or kidneys. Foods and medicines can change the color of urine. Pee is your body’s liquid waste, mainly. Your kidneys make urine by filtering wastes and extra water from your blood. From the kidneys, urine travels down. The waste is called urea. But a color change also could be a sign of disease. But the basic details of your urine — color, smell, and how often you go — can give you a hint about what’s going on inside your body. Describes how the urinary tract works, why it’s important, what affects the amount of urine produced, and how to keep the urinary tract healthy. Your kidneys make urine by filtering wastes and extra water from your blood. Your urine is a mix of water, electrolytes and waste that your kidneys filter out from your blood. Pee is your body’s liquid waste, mainly. Urine is liquid waste that your kidneys make to remove excess fluids and waste products from your body. From the kidneys, urine travels down. This article looks at what different urine colors may mean and when to contact a. Foods and medicines can change the color of urine. Some urine color changes may be a sign of an infection or a problem with the liver or kidneys. From the kidneys, urine travels down. But a color change also could be a sign of disease. Foods and medicines can change the color of urine. The color, odor, density, and frequency of your urine can tell you a lot about your health, as can the presence of proteins and ketones. Your urine is a mix of water, electrolytes and. The color, odor, density, and frequency of your urine can tell you a lot about your health, as can the presence of proteins and ketones. Your kidneys make urine by filtering wastes and extra water from your blood. From the kidneys, urine travels down. This article looks at what different urine colors may mean and when to contact a. When. Pee is your body’s liquid waste, mainly. Urine is liquid waste that your kidneys make to remove excess fluids and waste products from your body. The waste is called urea. Foods and medicines can change the color of urine. But the basic details of your urine — color, smell, and how often you go — can give you a hint. It mostly consists of water, but it also contains waste products, salt. Pee is your body’s liquid waste, mainly. Urine is liquid waste that your kidneys make to remove excess fluids and waste products from your body. Your kidneys make urine by filtering wastes and extra water from your blood. This article looks at what different urine colors may mean. Describes how the urinary tract works, why it’s important, what affects the amount of urine produced, and how to keep the urinary tract healthy. Foods and medicines can change the color of urine. Pee is your body’s liquid waste, mainly. It mostly consists of water, but it also contains waste products, salt. From the kidneys, urine travels down. Your kidneys make urine by filtering wastes and extra water from your blood. The waste is called urea. Your urine is a mix of water, electrolytes and waste that your kidneys filter out from your blood. This article looks at what different urine colors may mean and when to contact a. From the kidneys, urine travels down. It mostly consists of water, but it also contains waste products, salt. Your blood carries it to the kidneys. Describes how the urinary tract works, why it’s important, what affects the amount of urine produced, and how to keep the urinary tract healthy. The color, odor, density, and frequency of your urine can tell you a lot about your health,. Urine, liquid or semisolid solution of metabolic wastes and certain other, often toxic, substances that the excretory organs withdraw from the circulatory fluids and expel from the. Pee is your body’s liquid waste, mainly. Describes how the urinary tract works, why it’s important, what affects the amount of urine produced, and how to keep the urinary tract healthy. Your blood. The waste is called urea. Urine, liquid or semisolid solution of metabolic wastes and certain other, often toxic, substances that the excretory organs withdraw from the circulatory fluids and expel from the. Your urine is a mix of water, electrolytes and waste that your kidneys filter out from your blood. Some urine color changes may be a sign of an. Some urine color changes may be a sign of an infection or a problem with the liver or kidneys. Pee is your body’s liquid waste, mainly. It mostly consists of water, but it also contains waste products, salt. The waste is called urea. But a color change also could be a sign of disease. But the basic details of your urine — color, smell, and how often you go — can give you a hint about what’s going on inside your body. Pee is your body’s liquid waste, mainly. When you’re healthy and hydrated, your urine should fall somewhere between. This article looks at what different urine colors may mean and when to contact a. The waste is called urea. It mostly consists of water, but it also contains waste products, salt. Urine is liquid waste that your kidneys make to remove excess fluids and waste products from your body. Your blood carries it to the kidneys. Urine, liquid or semisolid solution of metabolic wastes and certain other, often toxic, substances that the excretory organs withdraw from the circulatory fluids and expel from the. Foods and medicines can change the color of urine. The color, odor, density, and frequency of your urine can tell you a lot about your health, as can the presence of proteins and ketones. From the kidneys, urine travels down. Describes how the urinary tract works, why it’s important, what affects the amount of urine produced, and how to keep the urinary tract healthy.Ph Of Urine
Ph Level Chart For Urine Urine Ph Normal Range
Urine PH (Normal PH Levels, Range, Chart) Causes Of, 40 OFF
Urine Ph Color Chart
Ph Level Chart For Urine Urine Ph Normal Range
Urine PH Chart
Urine Ph Level Color Chart
Ph Of Urine
Urine Ph Color Chart
Urine PH (Normal PH Levels, Range, Chart) Causes Of, 60 OFF
Your Urine Is A Mix Of Water, Electrolytes And Waste That Your Kidneys Filter Out From Your Blood.
But A Color Change Also Could Be A Sign Of Disease.
Your Kidneys Make Urine By Filtering Wastes And Extra Water From Your Blood.
Some Urine Color Changes May Be A Sign Of An Infection Or A Problem With The Liver Or Kidneys.
Related Post: