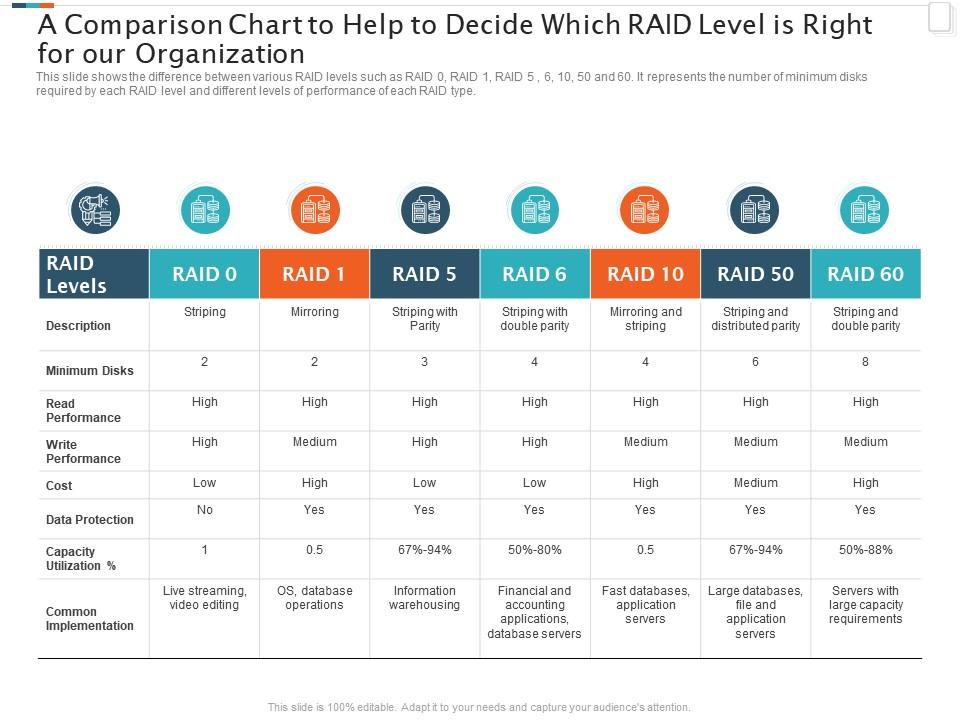
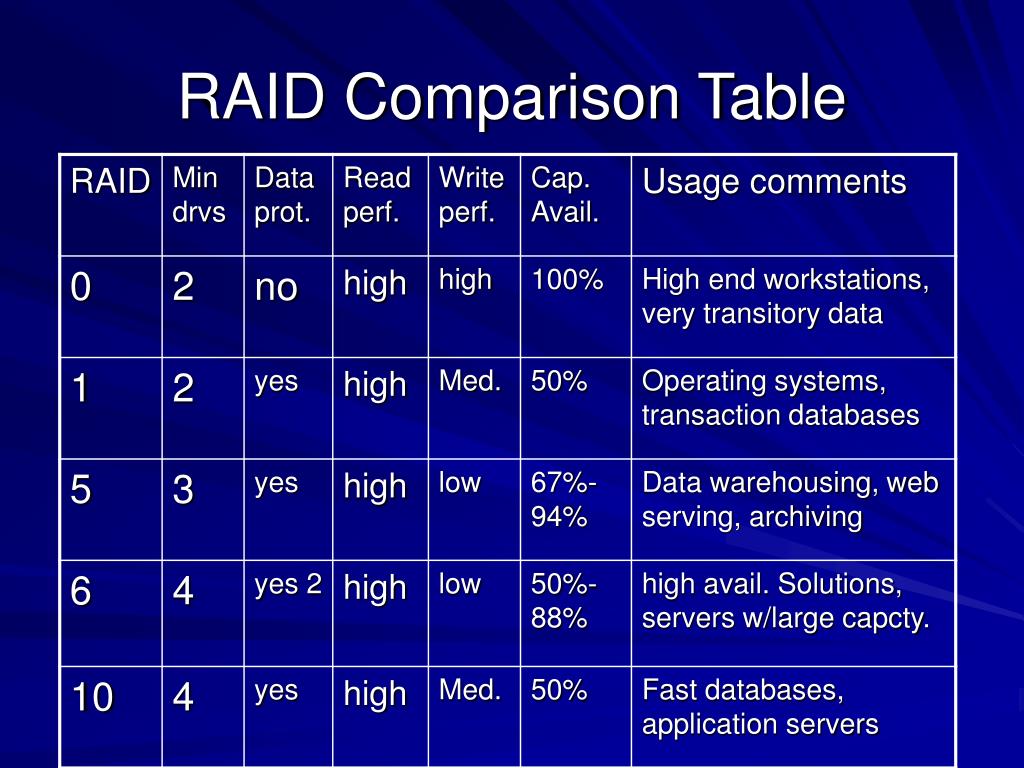
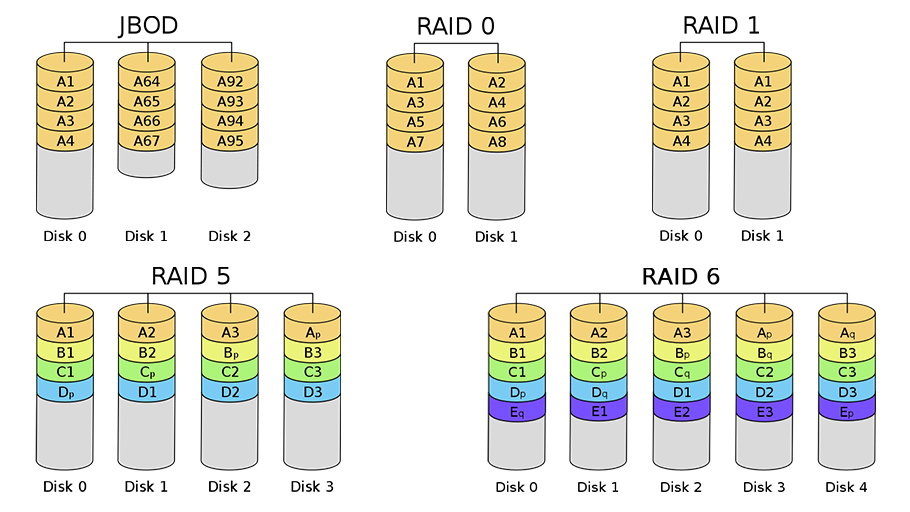
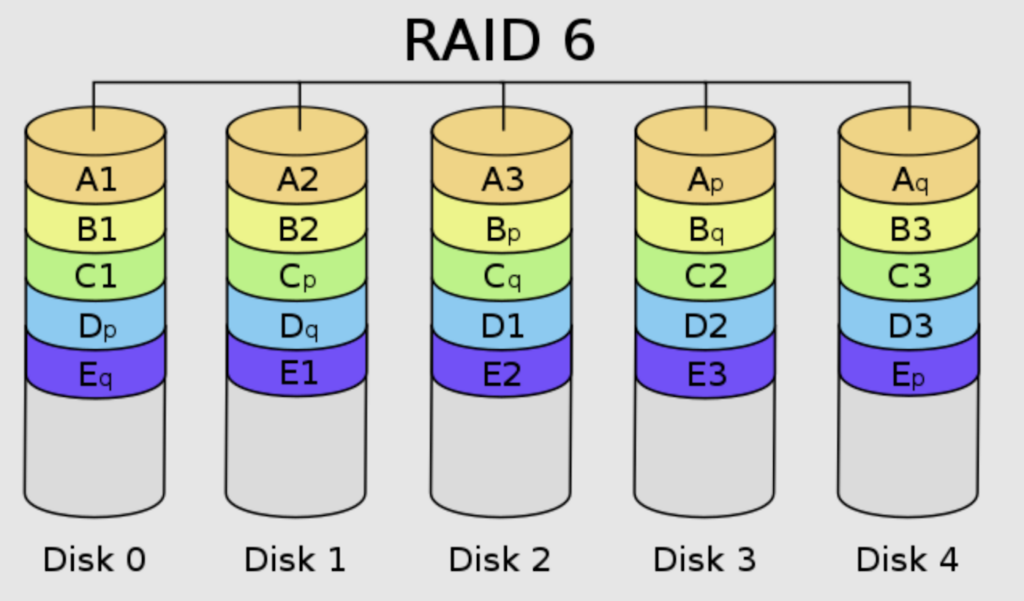
Raid Configurations Chart
Raid Configurations Chart - Raid is a data storage arrangement that combines multiple physical drives into one logical unit. Short tutorial on raid levels 0, 1, 5, 6 and 10, the advantages of striping, mirroring and parity for performance & security plus their use for prepress storage Raid (redundant array of independent disks) in a database management system (dbms) is a technology that combines multiple physical disk drives into a single logical unit for. Redundant array of inexpensive disks or redundant array of independent disks) [1][2] is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical data storage. The setup aims to improve storage performance, provide fault tolerance, or. Short tutorial on raid levels 0, 1, 5, 6 and 10, the advantages of striping, mirroring and parity for performance & security plus their use for prepress storage Raid (redundant array of independent disks) in a database management system (dbms) is a technology that combines multiple physical disk drives into a single logical unit for. Redundant array of inexpensive disks or redundant array of independent disks) [1][2] is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical data storage. Raid is a data storage arrangement that combines multiple physical drives into one logical unit. The setup aims to improve storage performance, provide fault tolerance, or. Short tutorial on raid levels 0, 1, 5, 6 and 10, the advantages of striping, mirroring and parity for performance & security plus their use for prepress storage The setup aims to improve storage performance, provide fault tolerance, or. Raid is a data storage arrangement that combines multiple physical drives into one logical unit. Redundant array of inexpensive disks or. Raid (redundant array of independent disks) in a database management system (dbms) is a technology that combines multiple physical disk drives into a single logical unit for. Short tutorial on raid levels 0, 1, 5, 6 and 10, the advantages of striping, mirroring and parity for performance & security plus their use for prepress storage Raid is a data storage. Raid (redundant array of independent disks) in a database management system (dbms) is a technology that combines multiple physical disk drives into a single logical unit for. Redundant array of inexpensive disks or redundant array of independent disks) [1][2] is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical data storage. The setup aims to improve storage performance, provide fault. Short tutorial on raid levels 0, 1, 5, 6 and 10, the advantages of striping, mirroring and parity for performance & security plus their use for prepress storage Raid is a data storage arrangement that combines multiple physical drives into one logical unit. Raid (redundant array of independent disks) in a database management system (dbms) is a technology that combines. Short tutorial on raid levels 0, 1, 5, 6 and 10, the advantages of striping, mirroring and parity for performance & security plus their use for prepress storage Redundant array of inexpensive disks or redundant array of independent disks) [1][2] is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical data storage. Raid (redundant array of independent disks) in a. Raid (redundant array of independent disks) in a database management system (dbms) is a technology that combines multiple physical disk drives into a single logical unit for. The setup aims to improve storage performance, provide fault tolerance, or. Redundant array of inexpensive disks or redundant array of independent disks) [1][2] is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical. Redundant array of inexpensive disks or redundant array of independent disks) [1][2] is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical data storage. Short tutorial on raid levels 0, 1, 5, 6 and 10, the advantages of striping, mirroring and parity for performance & security plus their use for prepress storage The setup aims to improve storage performance, provide. Raid is a data storage arrangement that combines multiple physical drives into one logical unit. Raid (redundant array of independent disks) in a database management system (dbms) is a technology that combines multiple physical disk drives into a single logical unit for. Redundant array of inexpensive disks or redundant array of independent disks) [1][2] is a data storage virtualization technology. The setup aims to improve storage performance, provide fault tolerance, or. Raid is a data storage arrangement that combines multiple physical drives into one logical unit. Short tutorial on raid levels 0, 1, 5, 6 and 10, the advantages of striping, mirroring and parity for performance & security plus their use for prepress storage Redundant array of inexpensive disks or. Raid is a data storage arrangement that combines multiple physical drives into one logical unit. The setup aims to improve storage performance, provide fault tolerance, or. Raid (redundant array of independent disks) in a database management system (dbms) is a technology that combines multiple physical disk drives into a single logical unit for. Redundant array of inexpensive disks or redundant. Short tutorial on raid levels 0, 1, 5, 6 and 10, the advantages of striping, mirroring and parity for performance & security plus their use for prepress storage Redundant array of inexpensive disks or redundant array of independent disks) [1][2] is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical data storage. The setup aims to improve storage performance, provide fault tolerance, or. Raid (redundant array of independent disks) in a database management system (dbms) is a technology that combines multiple physical disk drives into a single logical unit for.Understanding Raid Levels
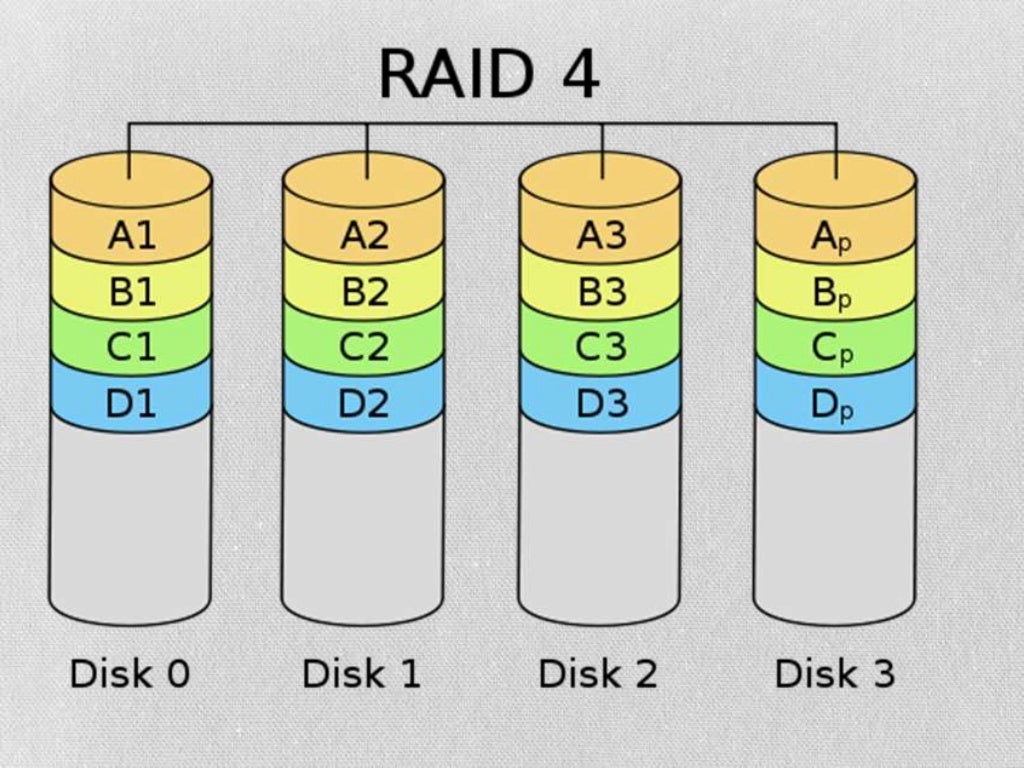
Differences Between RAID Configurations Aesonlabs®
RAID Levels Explained (2025) DiskInternals
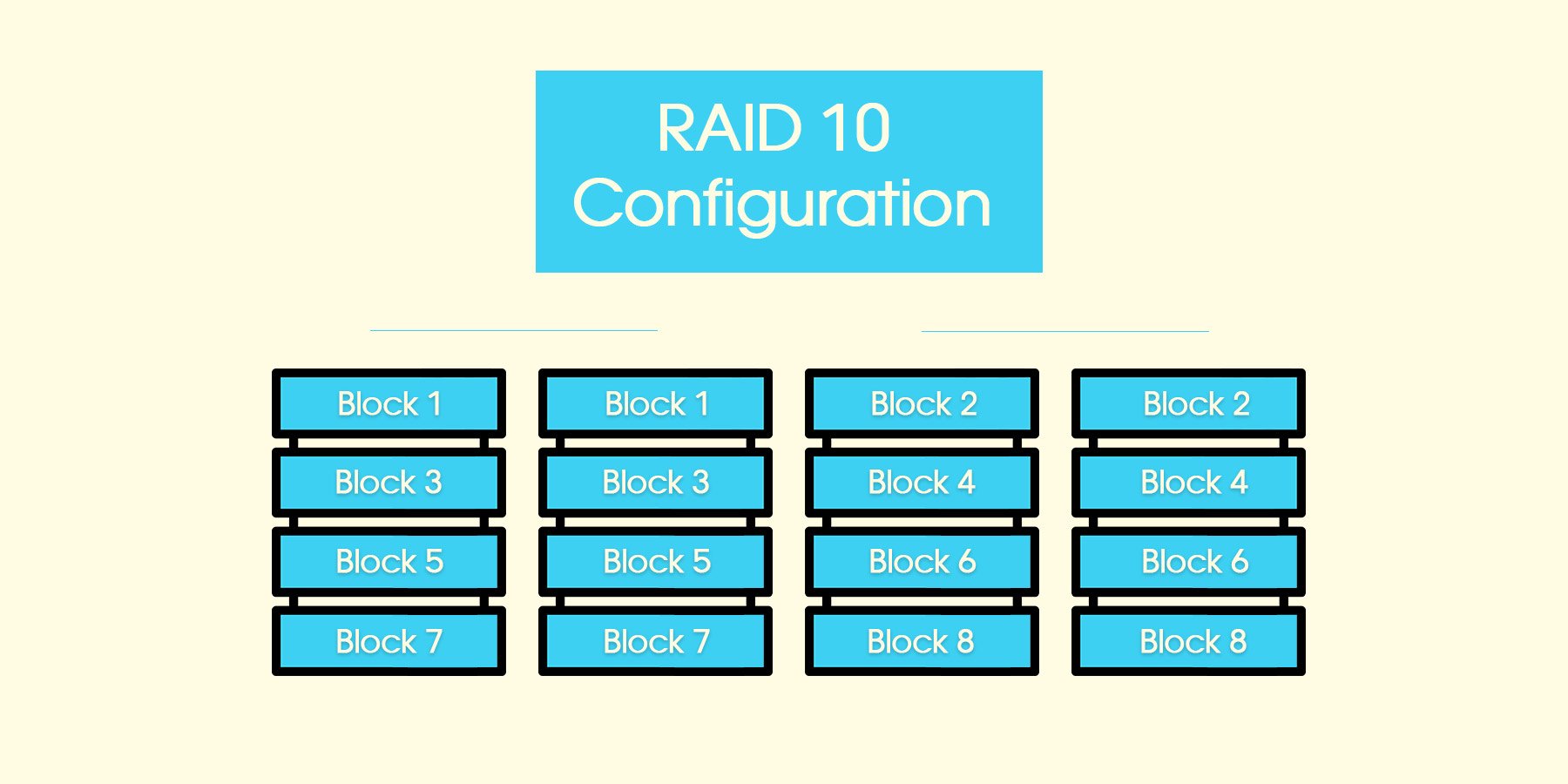
Understanding Raid Levels
Understanding Raid Levels
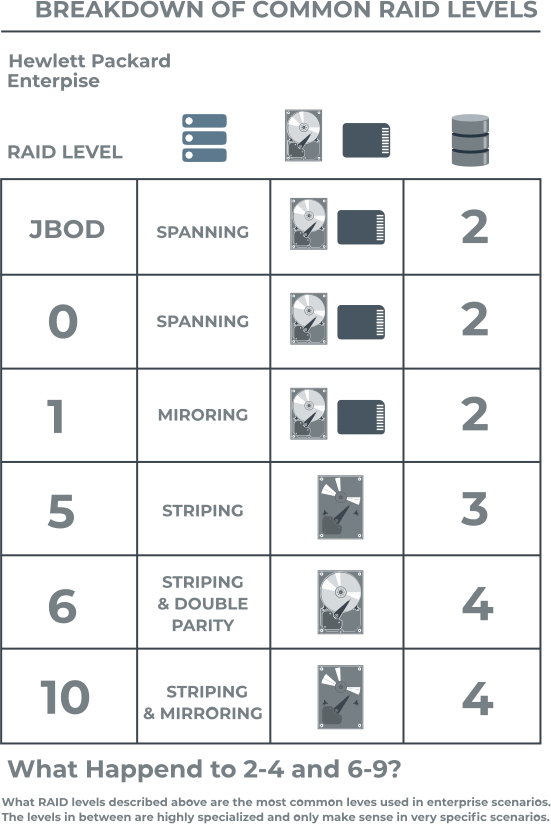
NAS RAID Levels Explained Which Level Is Right For You
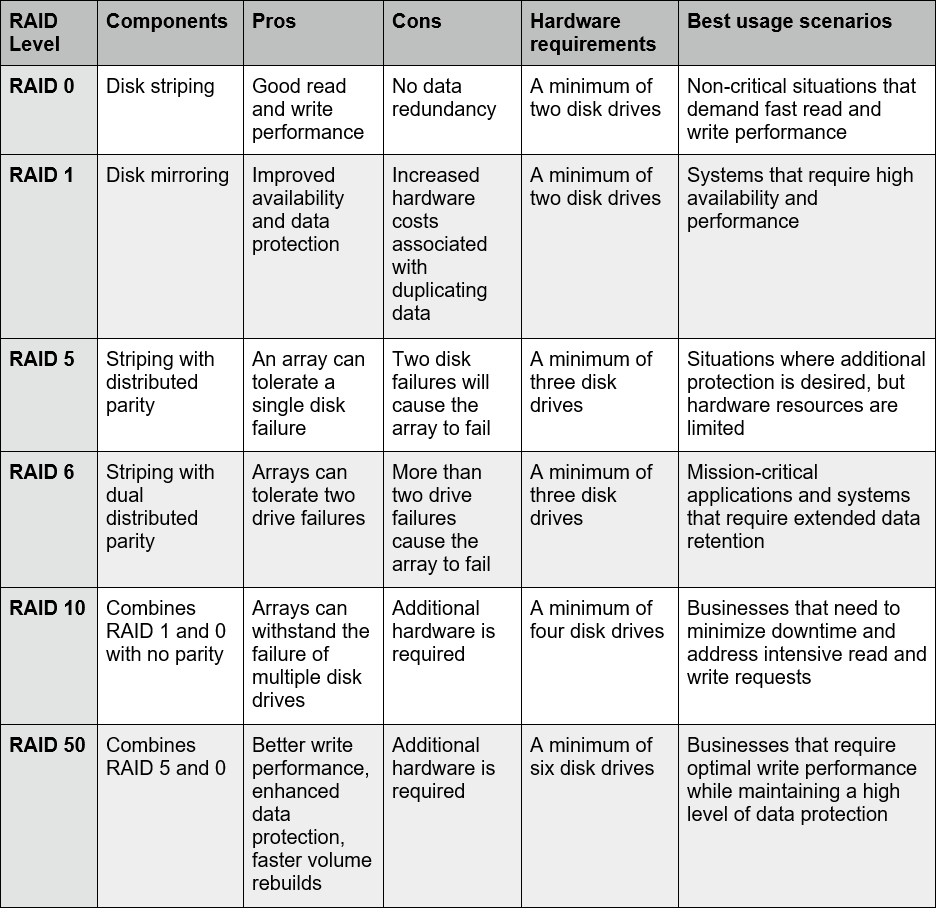
Raid Speed Comparison Chart
A Beginner’s Guide to JBOD and RAID Configurations Understanding Striping, Mirroring, and
RAID 5 vs RAID 6 How to Choose the Best RAID Configuration Petri
NAS RAID Levels Explained Which Level Is Right For You
Raid Is A Data Storage Arrangement That Combines Multiple Physical Drives Into One Logical Unit.
Related Post: