Polymers And Monomers Chart
Polymers And Monomers Chart - Polymers are long chain, giant organic molecules are assembled from many smaller molecules called monomers. Polymers can be found all around us, from the strand of our dna, which is a naturally occurring biopolymer, to polypropylene which is used throughout the world as plastic. Polymers consist of many repeating monomer units in long chains,. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as dna and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymer, any of a class of natural or synthetic substances composed of very large molecules, called macromolecules, that are multiples of simpler chemical units called. In this article, we’ll expand on what a polymer is, its features, classifications, and examples. Polymers are substances composed of macromolecules, very large molecules with molecular weights ranging from a few thousand to as high as millions of grams/mole. Polymers can be found all around us, from the strand of our dna, which is a naturally occurring biopolymer, to polypropylene which is used throughout the world as plastic. Polymer, any of a class of natural or synthetic substances composed of very large molecules, called macromolecules, that are multiples of simpler chemical units called. In this article, we’ll expand on what a polymer is, its features, classifications, and examples. Polymers are long chain, giant organic molecules are assembled from many smaller molecules called monomers. Polymers are substances composed of macromolecules, very large molecules with molecular weights ranging from a few thousand to as high as millions of grams/mole. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as dna and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers consist of many repeating monomer units in long chains,. Polymers consist of many repeating monomer units in long chains,. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as dna and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers are long chain, giant organic molecules are assembled from many smaller molecules called monomers. Polymer, any of a class of natural or synthetic substances. Polymers can be found all around us, from the strand of our dna, which is a naturally occurring biopolymer, to polypropylene which is used throughout the world as plastic. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as dna and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. In this article, we’ll expand on. Polymers are long chain, giant organic molecules are assembled from many smaller molecules called monomers. Polymers consist of many repeating monomer units in long chains,. In this article, we’ll expand on what a polymer is, its features, classifications, and examples. Polymer, any of a class of natural or synthetic substances composed of very large molecules, called macromolecules, that are multiples. Polymer, any of a class of natural or synthetic substances composed of very large molecules, called macromolecules, that are multiples of simpler chemical units called. In this article, we’ll expand on what a polymer is, its features, classifications, and examples. Polymers are substances composed of macromolecules, very large molecules with molecular weights ranging from a few thousand to as high. Polymer, any of a class of natural or synthetic substances composed of very large molecules, called macromolecules, that are multiples of simpler chemical units called. Polymers are long chain, giant organic molecules are assembled from many smaller molecules called monomers. Polymers can be found all around us, from the strand of our dna, which is a naturally occurring biopolymer, to. Polymers are substances composed of macromolecules, very large molecules with molecular weights ranging from a few thousand to as high as millions of grams/mole. Polymers consist of many repeating monomer units in long chains,. Polymers can be found all around us, from the strand of our dna, which is a naturally occurring biopolymer, to polypropylene which is used throughout the. In this article, we’ll expand on what a polymer is, its features, classifications, and examples. Polymers are long chain, giant organic molecules are assembled from many smaller molecules called monomers. Polymers can be found all around us, from the strand of our dna, which is a naturally occurring biopolymer, to polypropylene which is used throughout the world as plastic. Polymers. Polymer, any of a class of natural or synthetic substances composed of very large molecules, called macromolecules, that are multiples of simpler chemical units called. Polymers are long chain, giant organic molecules are assembled from many smaller molecules called monomers. Polymers are substances composed of macromolecules, very large molecules with molecular weights ranging from a few thousand to as high. Polymers consist of many repeating monomer units in long chains,. Polymers are substances composed of macromolecules, very large molecules with molecular weights ranging from a few thousand to as high as millions of grams/mole. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as dna and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymer,. Polymers are substances composed of macromolecules, very large molecules with molecular weights ranging from a few thousand to as high as millions of grams/mole. Polymer, any of a class of natural or synthetic substances composed of very large molecules, called macromolecules, that are multiples of simpler chemical units called. Polymers consist of many repeating monomer units in long chains,. In. Polymers consist of many repeating monomer units in long chains,. Polymers are long chain, giant organic molecules are assembled from many smaller molecules called monomers. Polymers are substances composed of macromolecules, very large molecules with molecular weights ranging from a few thousand to as high as millions of grams/mole. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as dna and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. In this article, we’ll expand on what a polymer is, its features, classifications, and examples.Polymers And Monomers Chart
Polymers And Monomers Chart
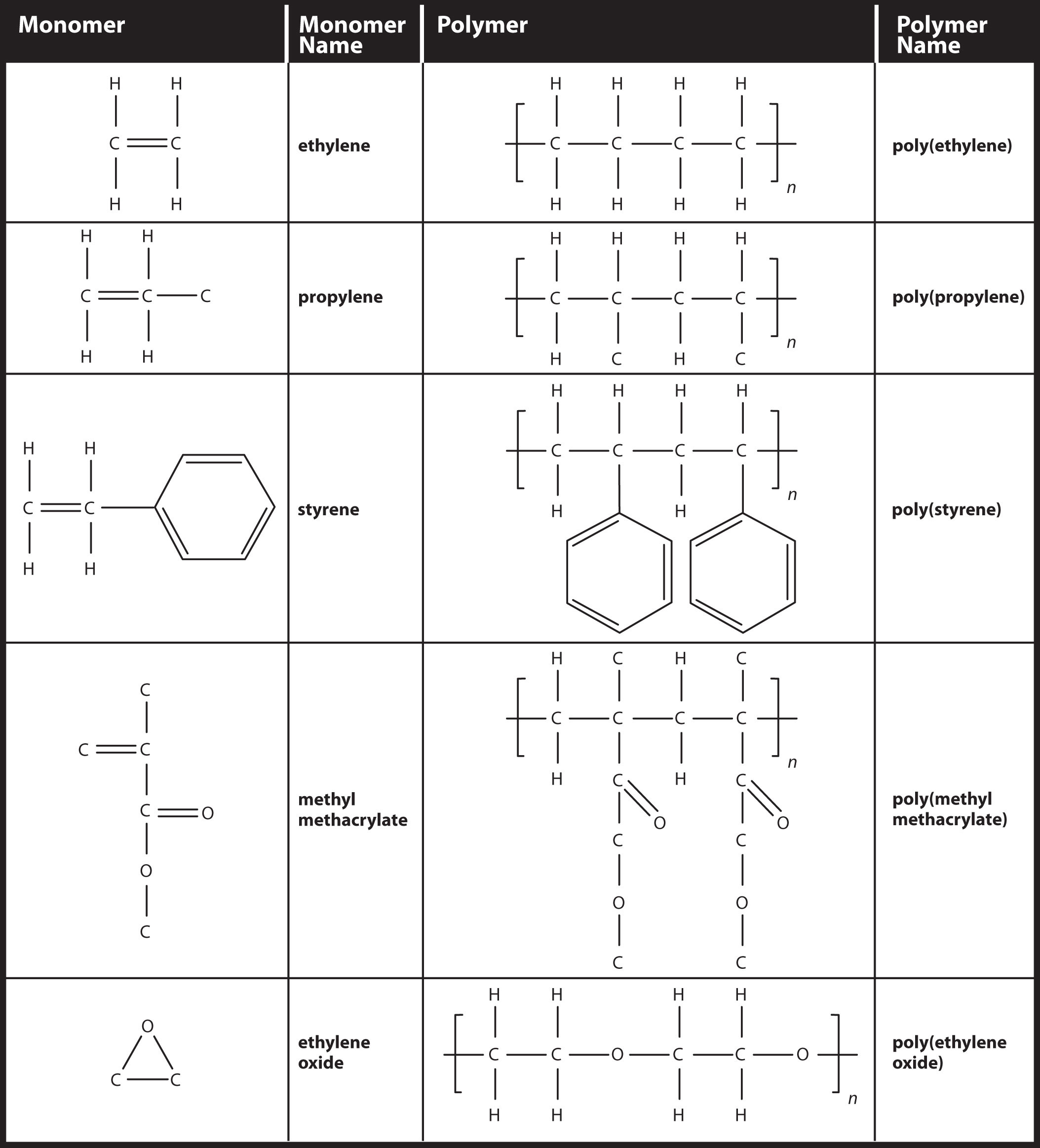
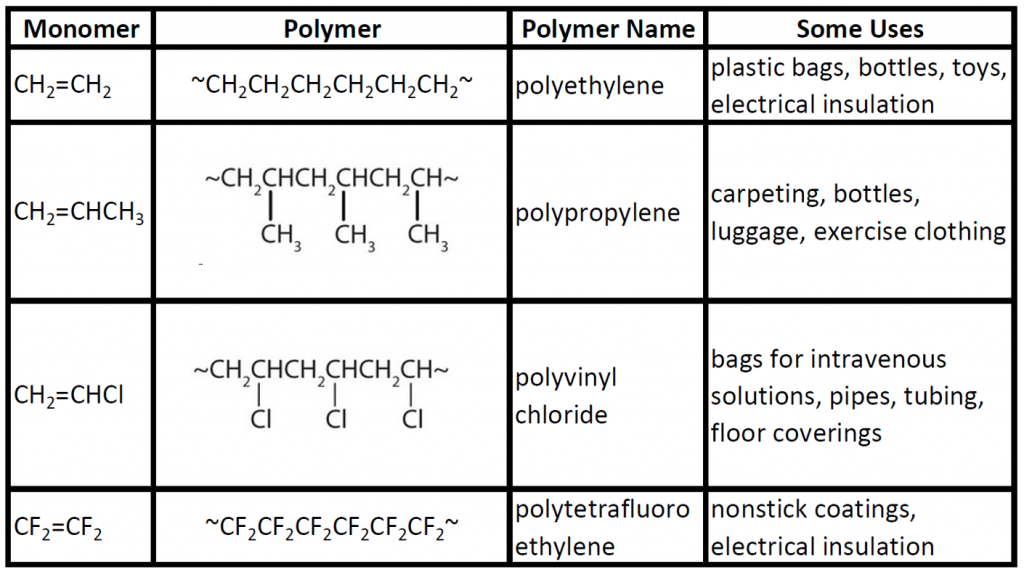
16.7 Polymers Chemistry LibreTexts
The Monomers That Make Up Lipids Are
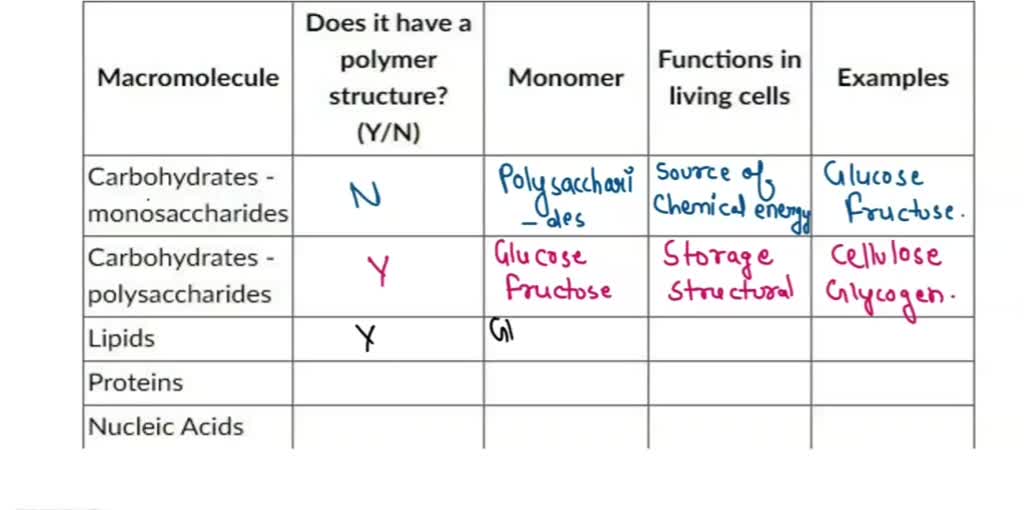
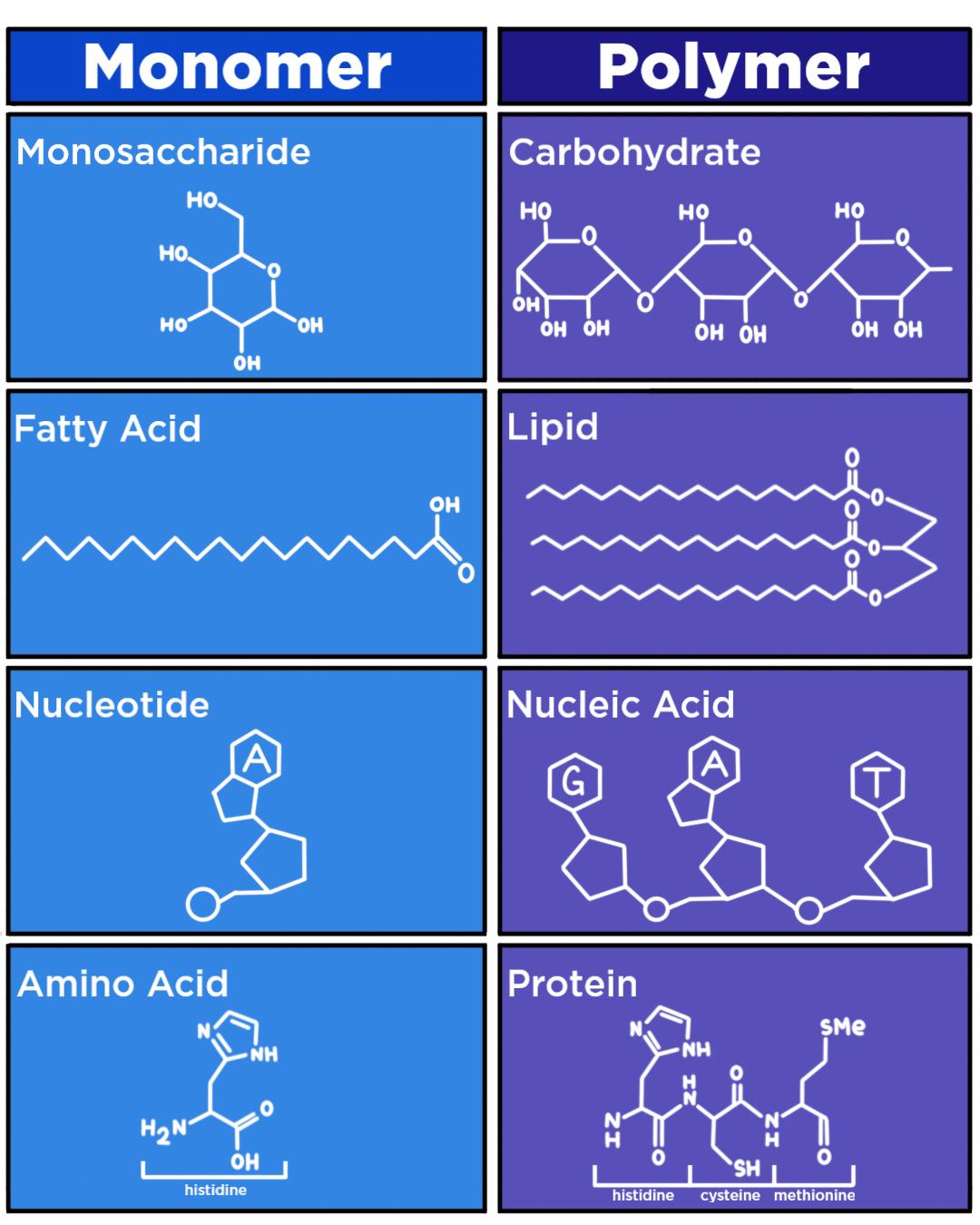
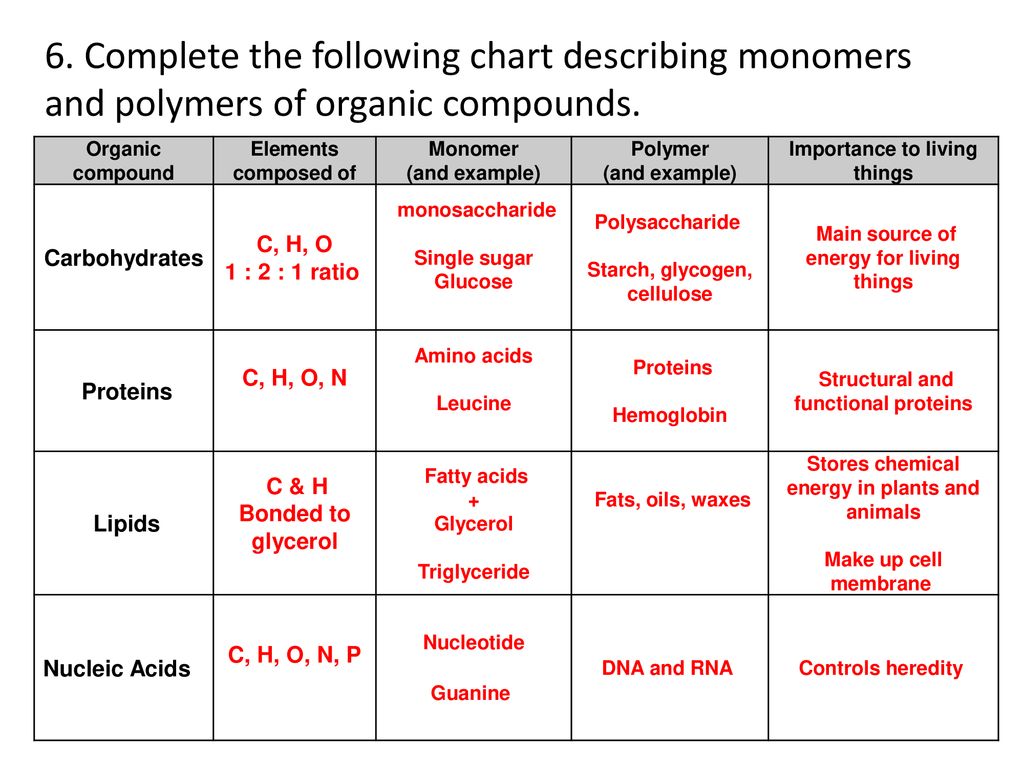
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Carbohydrates Biology classroom, Macromolecules
PPT CELL BIOLOGY (C) 2015 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5949047
Monomers And Polymers Of Proteins
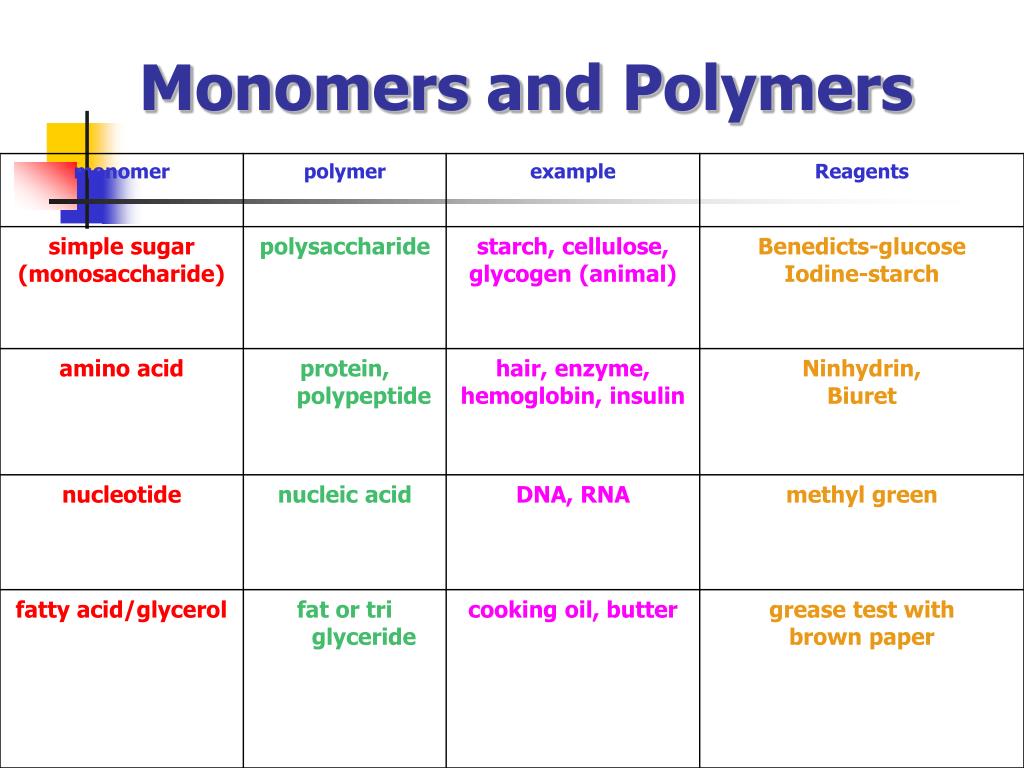
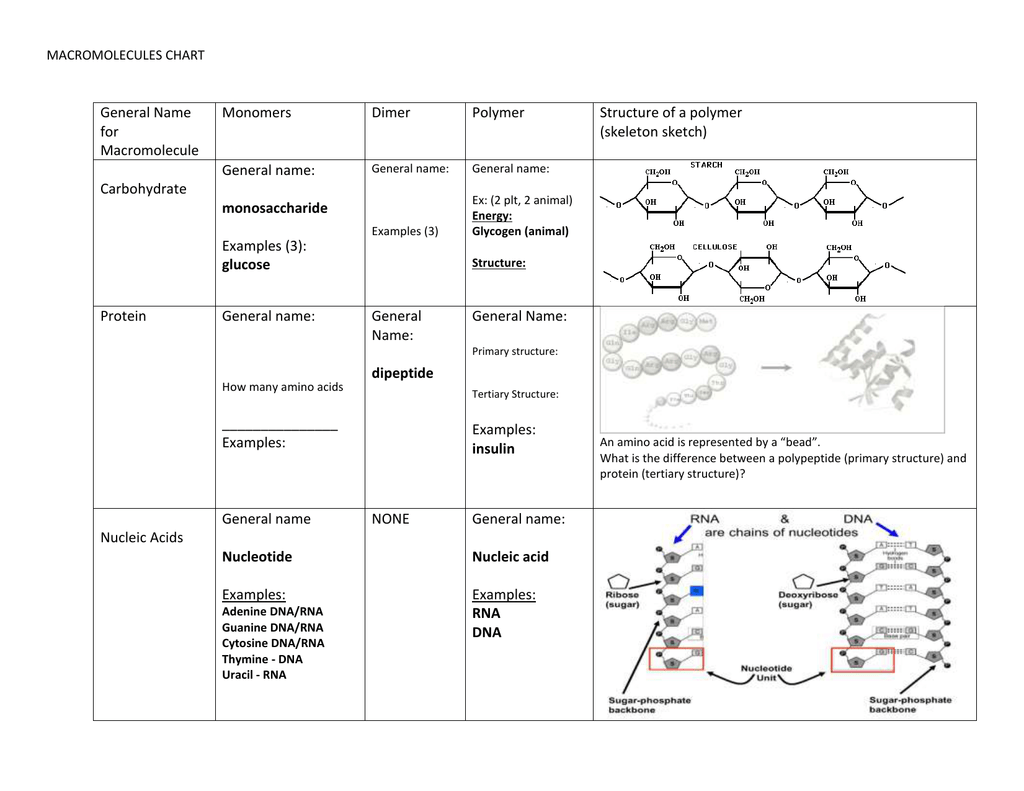
MACROMOLECULES CHART General Name for Macromolecule
Polymers And Monomers Chart
Worksheet Biochemistry ppt download
Polymers Can Be Found All Around Us, From The Strand Of Our Dna, Which Is A Naturally Occurring Biopolymer, To Polypropylene Which Is Used Throughout The World As Plastic.
Polymer, Any Of A Class Of Natural Or Synthetic Substances Composed Of Very Large Molecules, Called Macromolecules, That Are Multiples Of Simpler Chemical Units Called.
Related Post: