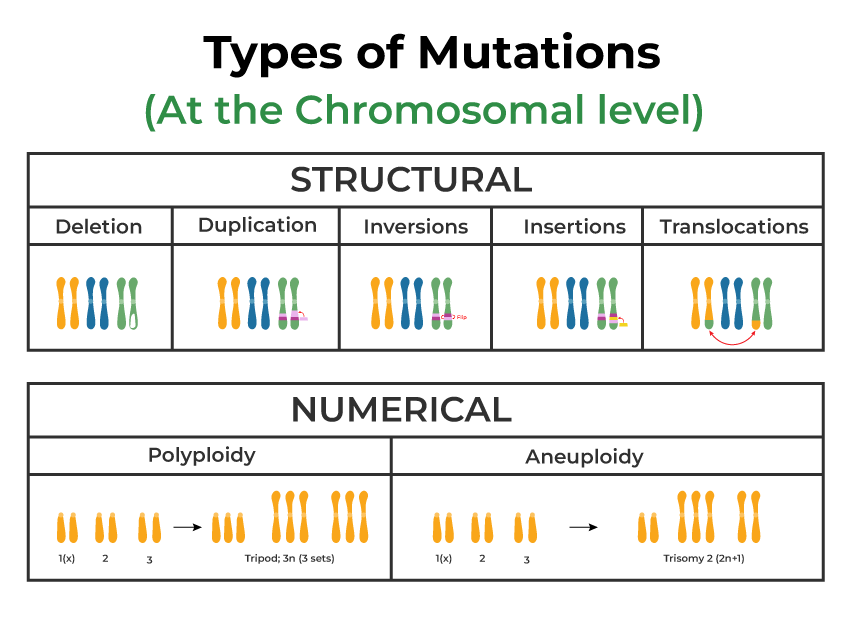
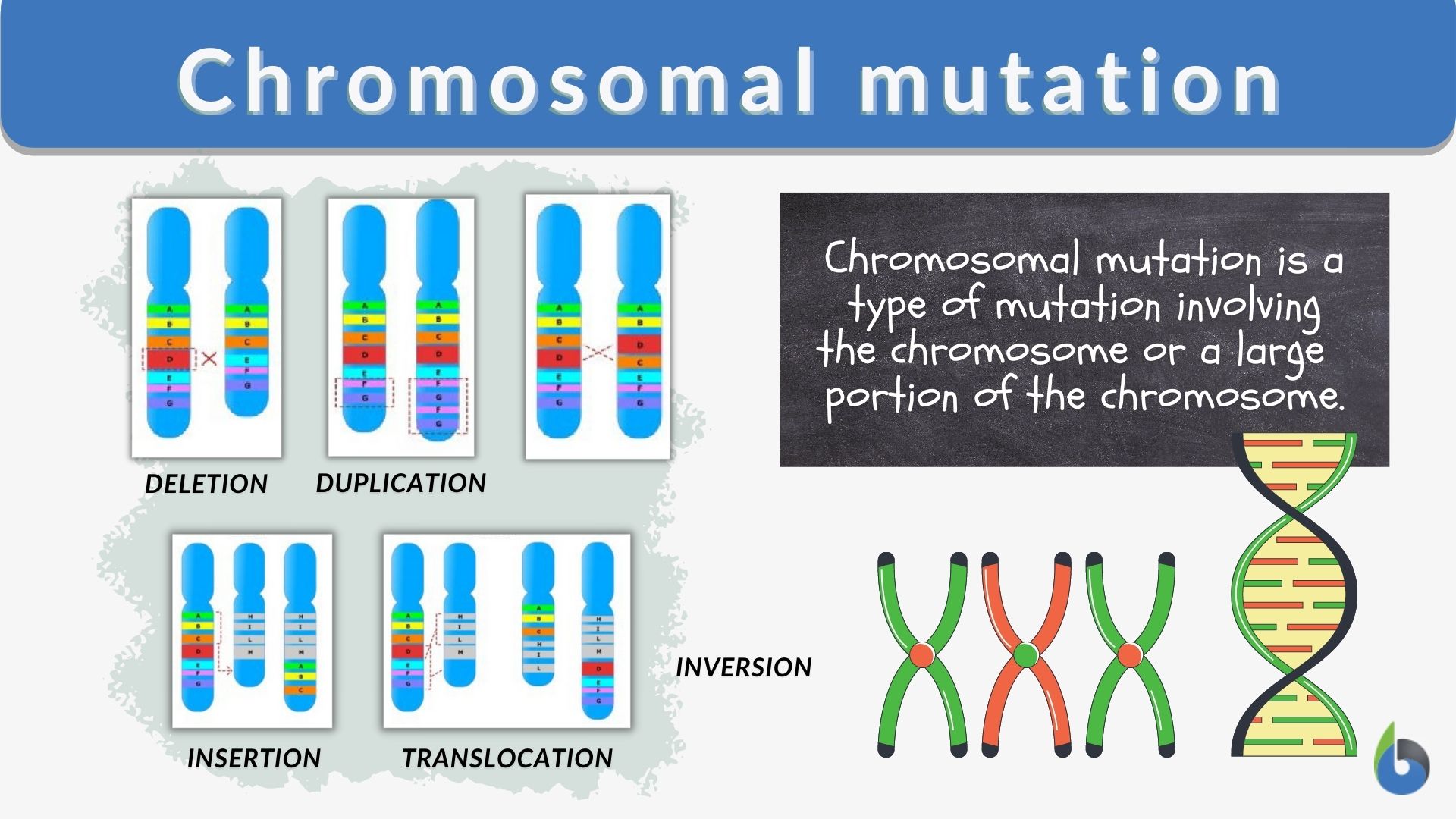
Mutation Chart
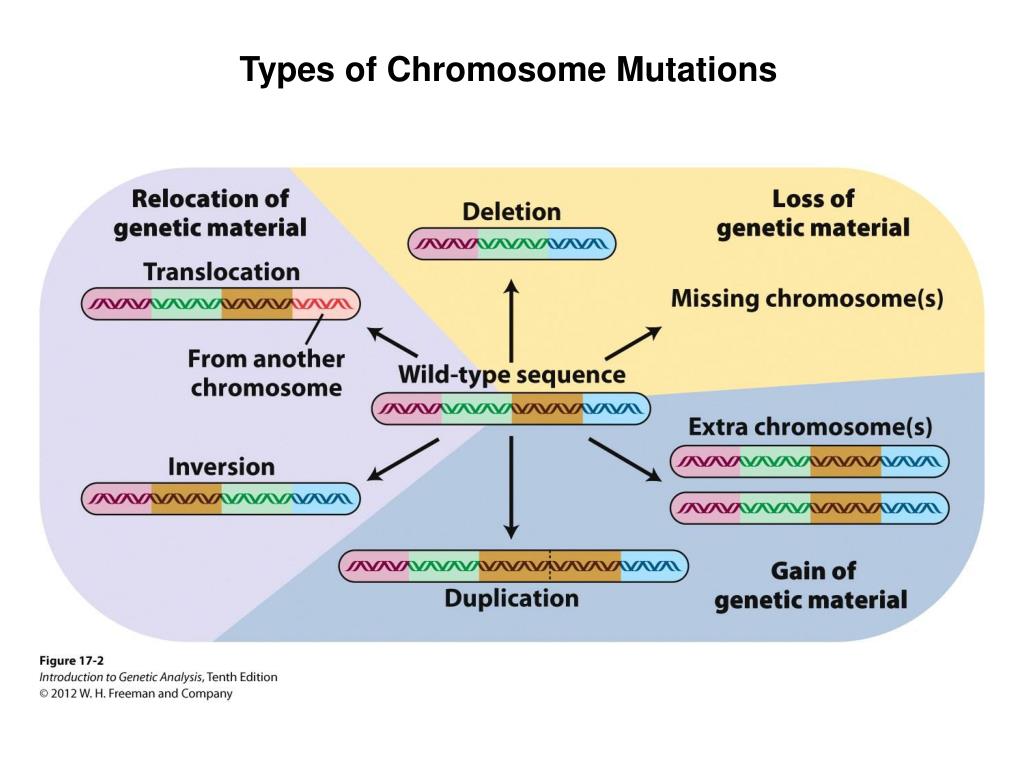
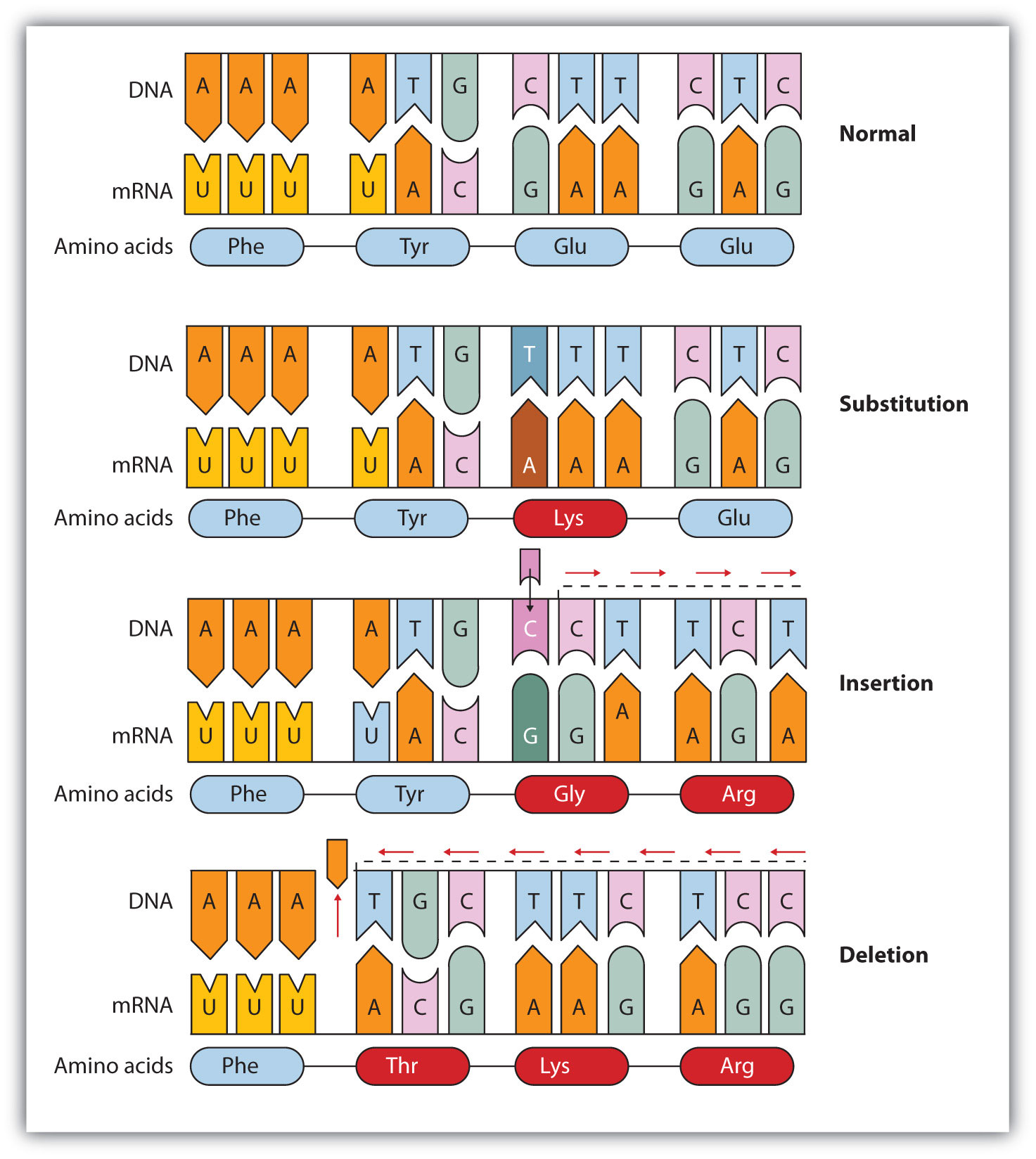
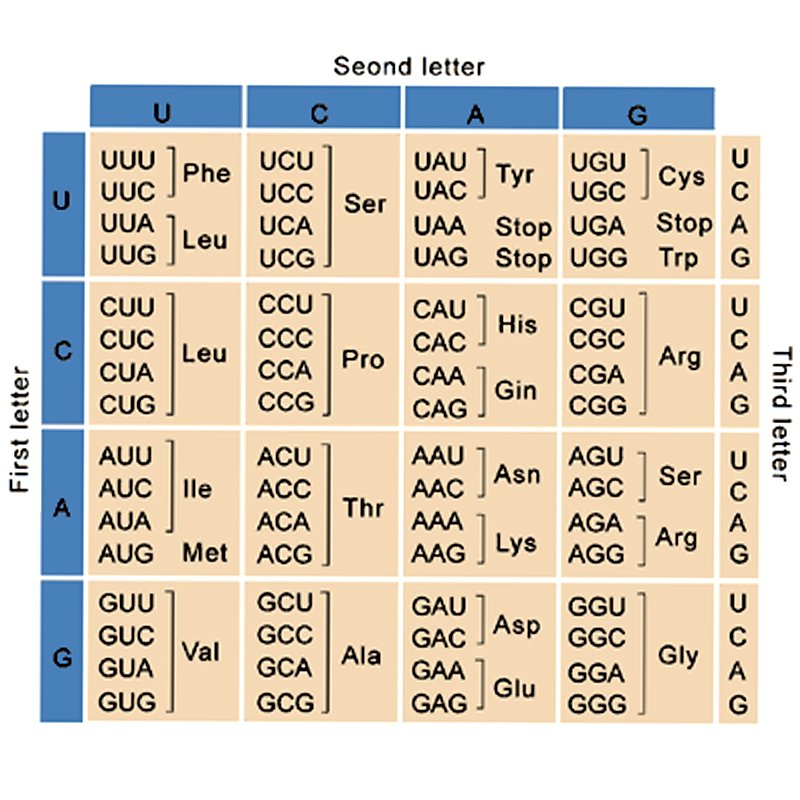
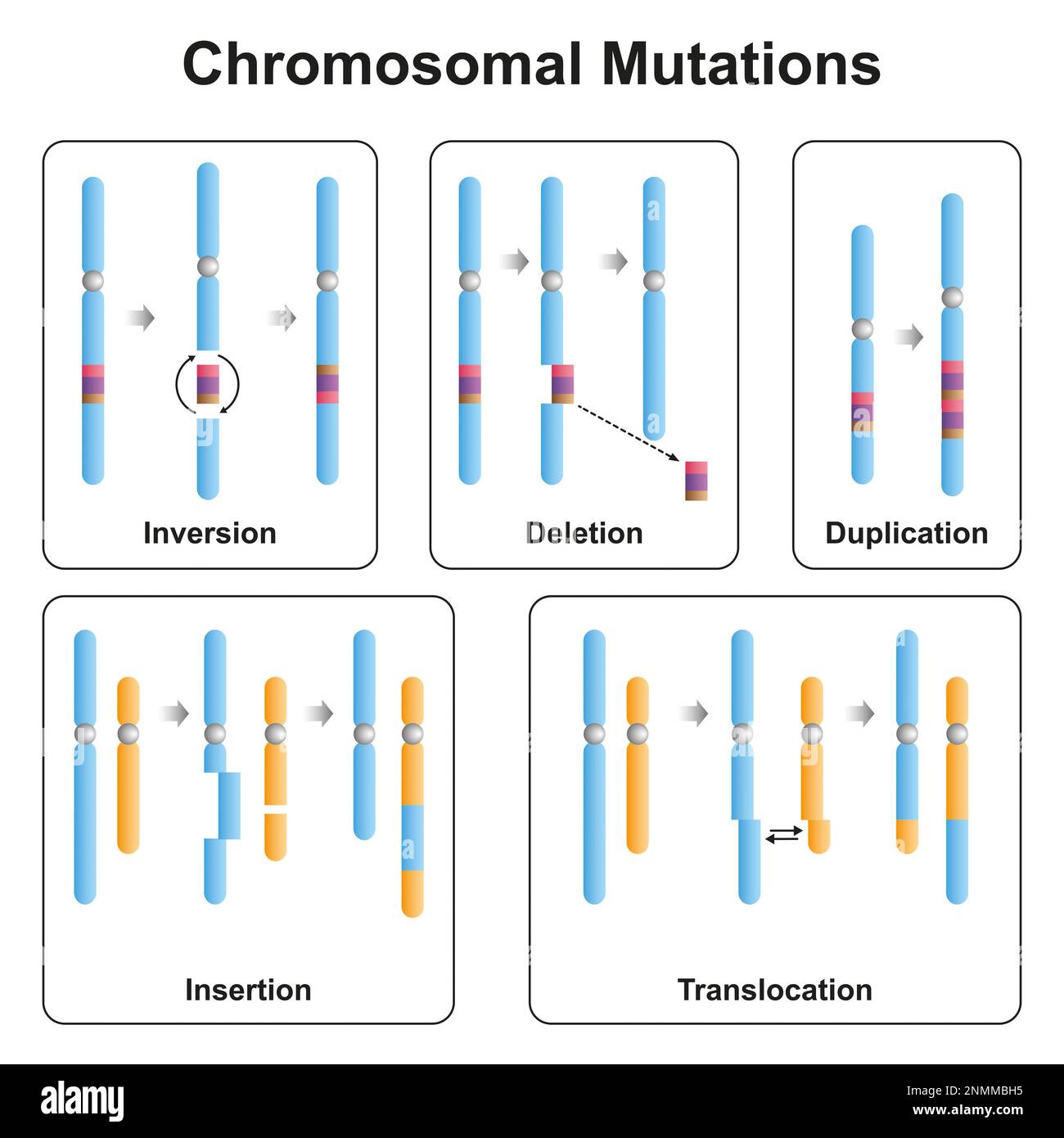
Mutation Chart - Your dna tells your body how to form. They account for the variation we. In biology, mutations refer to changes in chromosomes and genes, which typically manifest physically. Mutation creates slightly different versions of the same genes, called alleles. These alterations can occur spontaneously or be. Genetic mutations are changes in the dna sequence that can significantly affect an organism’s health and development. Mutation is a permanent change in the dna sequence of a gene or chromosome, which can result from errors in replication or environmental factors and can affect an. Mutation can result in many different. Genetic mutations are changes to your dna sequence that happen during cell division when your cells make copies of themselves. Mutations can result from dna copying mistakes made during cell division, exposure to ionizing radiation, exposure to chemicals. A mutation is a change in a dna sequence. They account for the variation we. Mutation is a permanent change in the dna sequence of a gene or chromosome, which can result from errors in replication or environmental factors and can affect an. Mutation is the ultimate source of all genetic variation, providing the raw material on which evolutionary forces such as natural selection can act. Mutation can result in many different. Your dna tells your body how to form. Mutations can result from dna copying mistakes made during cell division, exposure to ionizing radiation, exposure to chemicals. Genetic mutations are changes to your dna sequence that happen during cell division when your cells make copies of themselves. Genetic mutations are changes in the dna sequence that can significantly affect an organism’s health and development. At the simplest level, a mutation is a change or transformation. Genetic mutations are changes to your dna sequence that happen during cell division when your cells make copies of themselves. Mutation is a permanent change in the dna sequence of a gene or chromosome, which can result from errors in replication or environmental factors and can affect an. They account for the variation we. A mutation is a change in. Mutation creates slightly different versions of the same genes, called alleles. Mutation is the ultimate source of all genetic variation, providing the raw material on which evolutionary forces such as natural selection can act. These alterations can occur spontaneously or be. Your dna tells your body how to form. They account for the variation we. Mutations can result from dna copying mistakes made during cell division, exposure to ionizing radiation, exposure to chemicals. Mutation is the ultimate source of all genetic variation, providing the raw material on which evolutionary forces such as natural selection can act. Genetic mutations are changes to your dna sequence that happen during cell division when your cells make copies of. They account for the variation we. In biology, mutations refer to changes in chromosomes and genes, which typically manifest physically. A mutation is a change in a dna sequence. Mutation is the ultimate source of all genetic variation, providing the raw material on which evolutionary forces such as natural selection can act. At the simplest level, a mutation is a. Mutations can result from dna copying mistakes made during cell division, exposure to ionizing radiation, exposure to chemicals. These alterations can occur spontaneously or be. Mutation is the ultimate source of all genetic variation, providing the raw material on which evolutionary forces such as natural selection can act. Mutation creates slightly different versions of the same genes, called alleles. Genetic. Mutation is a permanent change in the dna sequence of a gene or chromosome, which can result from errors in replication or environmental factors and can affect an. Mutation is the ultimate source of all genetic variation, providing the raw material on which evolutionary forces such as natural selection can act. In biology, mutations refer to changes in chromosomes and. They account for the variation we. Genetic mutations are changes in the dna sequence that can significantly affect an organism’s health and development. At the simplest level, a mutation is a change or transformation. A mutation is a change in a dna sequence. These alterations can occur spontaneously or be. Genetic mutations are changes in the dna sequence that can significantly affect an organism’s health and development. These alterations can occur spontaneously or be. A mutation is a change in a dna sequence. Your dna tells your body how to form. Mutation creates slightly different versions of the same genes, called alleles. They account for the variation we. Your dna tells your body how to form. Genetic mutations are changes in the dna sequence that can significantly affect an organism’s health and development. Mutation creates slightly different versions of the same genes, called alleles. A mutation is a change in a dna sequence. Mutation is the ultimate source of all genetic variation, providing the raw material on which evolutionary forces such as natural selection can act. Genetic mutations are changes to your dna sequence that happen during cell division when your cells make copies of themselves. Mutations can result from dna copying mistakes made during cell division, exposure to ionizing radiation, exposure to. Genetic mutations are changes to your dna sequence that happen during cell division when your cells make copies of themselves. At the simplest level, a mutation is a change or transformation. These alterations can occur spontaneously or be. They account for the variation we. Mutation can result in many different. Mutation creates slightly different versions of the same genes, called alleles. In biology, mutations refer to changes in chromosomes and genes, which typically manifest physically. A mutation is a change in a dna sequence. Your dna tells your body how to form. Mutations can result from dna copying mistakes made during cell division, exposure to ionizing radiation, exposure to chemicals. These small differences in dna sequence make every individual unique.PPT Types of Chromosome Mutations PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5828495
Mutations and Diseases
Types Of Mutation Grade 12 at Thomas Lujan blog
mutations Science of Healthy
Mutation
Mutation Definition & Types (Missense, Nonsense, Deletion, Insertion Etc)
The Diagram Shows Three Types Of Mutations
Illustration of the different types of mutation Stock Photo Alamy
Mutation
Chromosomal mutation Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
Mutation Is A Permanent Change In The Dna Sequence Of A Gene Or Chromosome, Which Can Result From Errors In Replication Or Environmental Factors And Can Affect An.
Mutation Is The Ultimate Source Of All Genetic Variation, Providing The Raw Material On Which Evolutionary Forces Such As Natural Selection Can Act.
Genetic Mutations Are Changes In The Dna Sequence That Can Significantly Affect An Organism’s Health And Development.
Related Post: