Lysosomal Storage Diseases Chart
Lysosomal Storage Diseases Chart - Long known as terminal degradation stations, lysosomes have emerged as sophisticated signalling centres that govern cell growth, division and differentiation. They are located in the cytosol of the cells, floating freely within the cells outside the nucleus. Lysosome, subcellular organelle that is found in nearly all types of eukaryotic cells (cells with a clearly defined nucleus) and that is responsible for the digestion of. Lysosomes dispose and recycle extracellular or intracellular macromolecules by. Their primary responsibility is catabolic degradation of proteins,. Lysosomes are the main proteolytic compartments of mammalian cells comprising of a battery of hydrolases. Lysosomes are involved with various cell processes. Cellular metabolism, cell proliferation and differentiation, immunity, and cell death. There are normally hundreds of lysosomes in the cytosol, where they function as the cell’s degradation center. Here, we summarize current knowledge of the regulatory mechanisms of lysosome biogenesis, including synthesis of lysosomal proteins and their delivery via the endosome. Cellular metabolism, cell proliferation and differentiation, immunity, and cell death. In this review, we interpreted the key biological functions of lysosomes in four areas: They are located in the cytosol of the cells, floating freely within the cells outside the nucleus. Lysosomes are the main proteolytic compartments of mammalian cells comprising of a battery of hydrolases. Their primary responsibility is catabolic degradation of proteins,. Here, we summarize current knowledge of the regulatory mechanisms of lysosome biogenesis, including synthesis of lysosomal proteins and their delivery via the endosome. Long known as terminal degradation stations, lysosomes have emerged as sophisticated signalling centres that govern cell growth, division and differentiation. There are normally hundreds of lysosomes in the cytosol, where they function as the cell’s degradation center. Clinical presentationprovider resourcessymptoms of mps iiiatesting for mps iiia Lysosomes are involved with various cell processes. In this review, we interpreted the key biological functions of lysosomes in four areas: Here, we summarize current knowledge of the regulatory mechanisms of lysosome biogenesis, including synthesis of lysosomal proteins and their delivery via the endosome. They are located in the cytosol of the cells, floating freely within the cells outside the nucleus. Lysosomes dispose and recycle extracellular or. Lysosomes are the main proteolytic compartments of mammalian cells comprising of a battery of hydrolases. Lysosome, subcellular organelle that is found in nearly all types of eukaryotic cells (cells with a clearly defined nucleus) and that is responsible for the digestion of. Cellular metabolism, cell proliferation and differentiation, immunity, and cell death. Lysosomes are involved with various cell processes. They. Here, we summarize current knowledge of the regulatory mechanisms of lysosome biogenesis, including synthesis of lysosomal proteins and their delivery via the endosome. Lysosome, subcellular organelle that is found in nearly all types of eukaryotic cells (cells with a clearly defined nucleus) and that is responsible for the digestion of. Cellular metabolism, cell proliferation and differentiation, immunity, and cell death.. Lysosome, subcellular organelle that is found in nearly all types of eukaryotic cells (cells with a clearly defined nucleus) and that is responsible for the digestion of. Lysosomes dispose and recycle extracellular or intracellular macromolecules by. Cellular metabolism, cell proliferation and differentiation, immunity, and cell death. Lysosomes are the main proteolytic compartments of mammalian cells comprising of a battery of. Cellular metabolism, cell proliferation and differentiation, immunity, and cell death. Lysosomes are the main proteolytic compartments of mammalian cells comprising of a battery of hydrolases. Lysosome, subcellular organelle that is found in nearly all types of eukaryotic cells (cells with a clearly defined nucleus) and that is responsible for the digestion of. They are located in the cytosol of the. Here, we summarize current knowledge of the regulatory mechanisms of lysosome biogenesis, including synthesis of lysosomal proteins and their delivery via the endosome. In this review, we interpreted the key biological functions of lysosomes in four areas: Long known as terminal degradation stations, lysosomes have emerged as sophisticated signalling centres that govern cell growth, division and differentiation. Lysosome, subcellular organelle. Their primary responsibility is catabolic degradation of proteins,. Lysosome, subcellular organelle that is found in nearly all types of eukaryotic cells (cells with a clearly defined nucleus) and that is responsible for the digestion of. Lysosomes dispose and recycle extracellular or intracellular macromolecules by. Long known as terminal degradation stations, lysosomes have emerged as sophisticated signalling centres that govern cell. Lysosome, subcellular organelle that is found in nearly all types of eukaryotic cells (cells with a clearly defined nucleus) and that is responsible for the digestion of. Clinical presentationprovider resourcessymptoms of mps iiiatesting for mps iiia Long known as terminal degradation stations, lysosomes have emerged as sophisticated signalling centres that govern cell growth, division and differentiation. In this review, we. Clinical presentationprovider resourcessymptoms of mps iiiatesting for mps iiia In this review, we interpreted the key biological functions of lysosomes in four areas: Lysosomes are the main proteolytic compartments of mammalian cells comprising of a battery of hydrolases. Long known as terminal degradation stations, lysosomes have emerged as sophisticated signalling centres that govern cell growth, division and differentiation. Cellular metabolism,. Clinical presentationprovider resourcessymptoms of mps iiiatesting for mps iiia They are located in the cytosol of the cells, floating freely within the cells outside the nucleus. Here, we summarize current knowledge of the regulatory mechanisms of lysosome biogenesis, including synthesis of lysosomal proteins and their delivery via the endosome. Cellular metabolism, cell proliferation and differentiation, immunity, and cell death. Their. Cellular metabolism, cell proliferation and differentiation, immunity, and cell death. Lysosomes are the main proteolytic compartments of mammalian cells comprising of a battery of hydrolases. They are located in the cytosol of the cells, floating freely within the cells outside the nucleus. Lysosomes dispose and recycle extracellular or intracellular macromolecules by. Lysosomes are involved with various cell processes. Clinical presentationprovider resourcessymptoms of mps iiiatesting for mps iiia Their primary responsibility is catabolic degradation of proteins,. Lysosome, subcellular organelle that is found in nearly all types of eukaryotic cells (cells with a clearly defined nucleus) and that is responsible for the digestion of. There are normally hundreds of lysosomes in the cytosol, where they function as the cell’s degradation center.Lysosomal Storage Diseases. Download Table
Lysosomal Storage Diseases Chart
Classification of lysosomal storage disorders Download Scientific Diagram
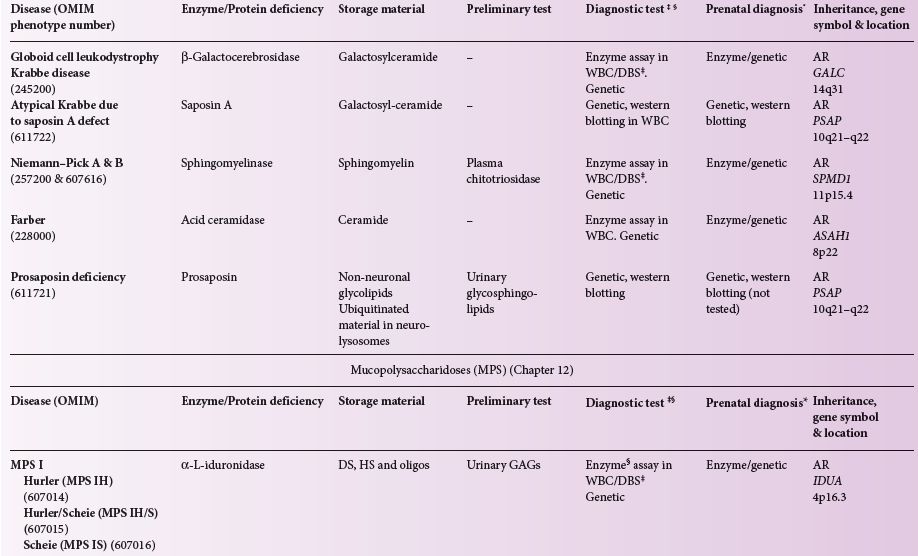
Most common types of lysosomal storage disorders. Download Table
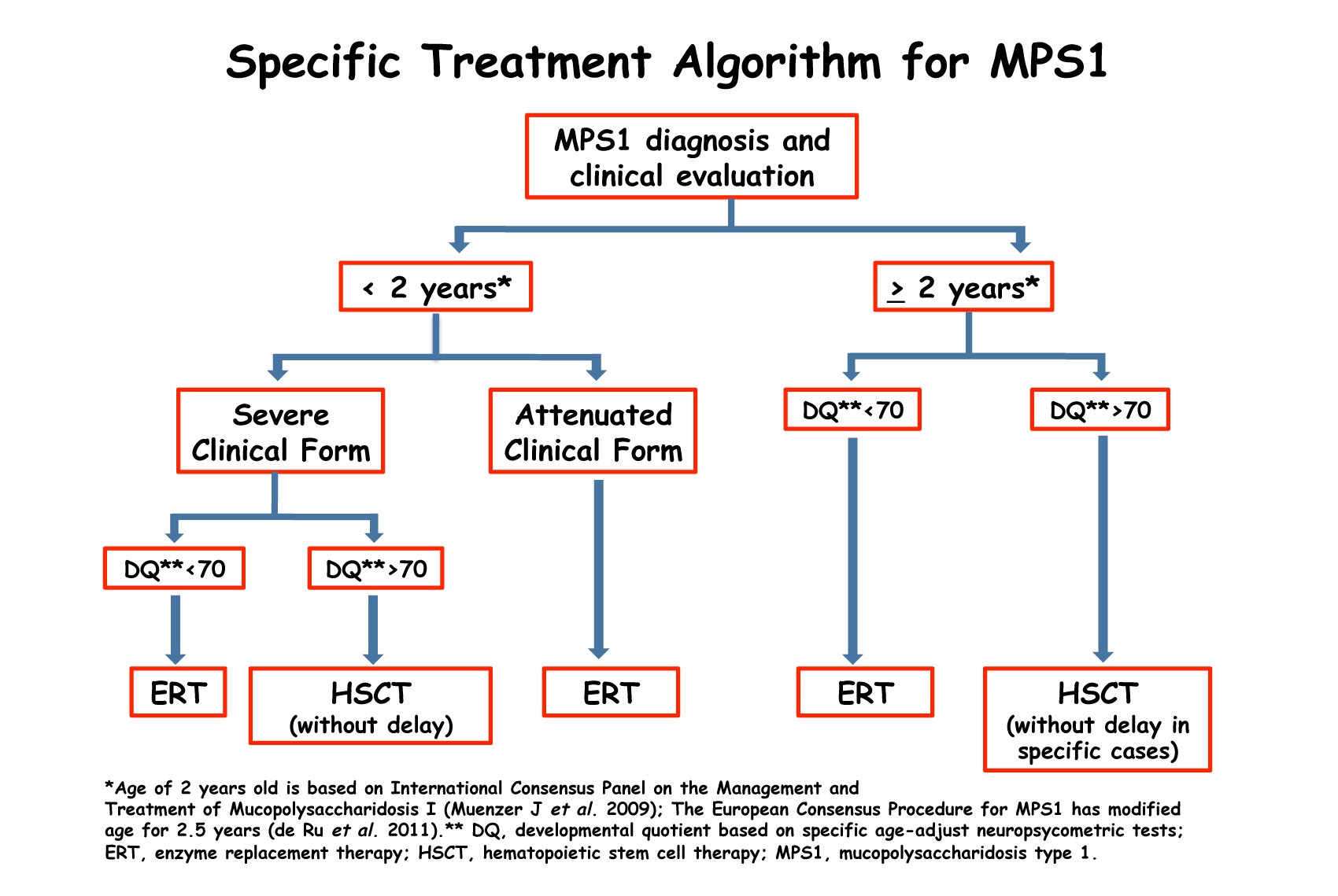
Lysosomal storage disease types, list, causes, symptoms & treatment
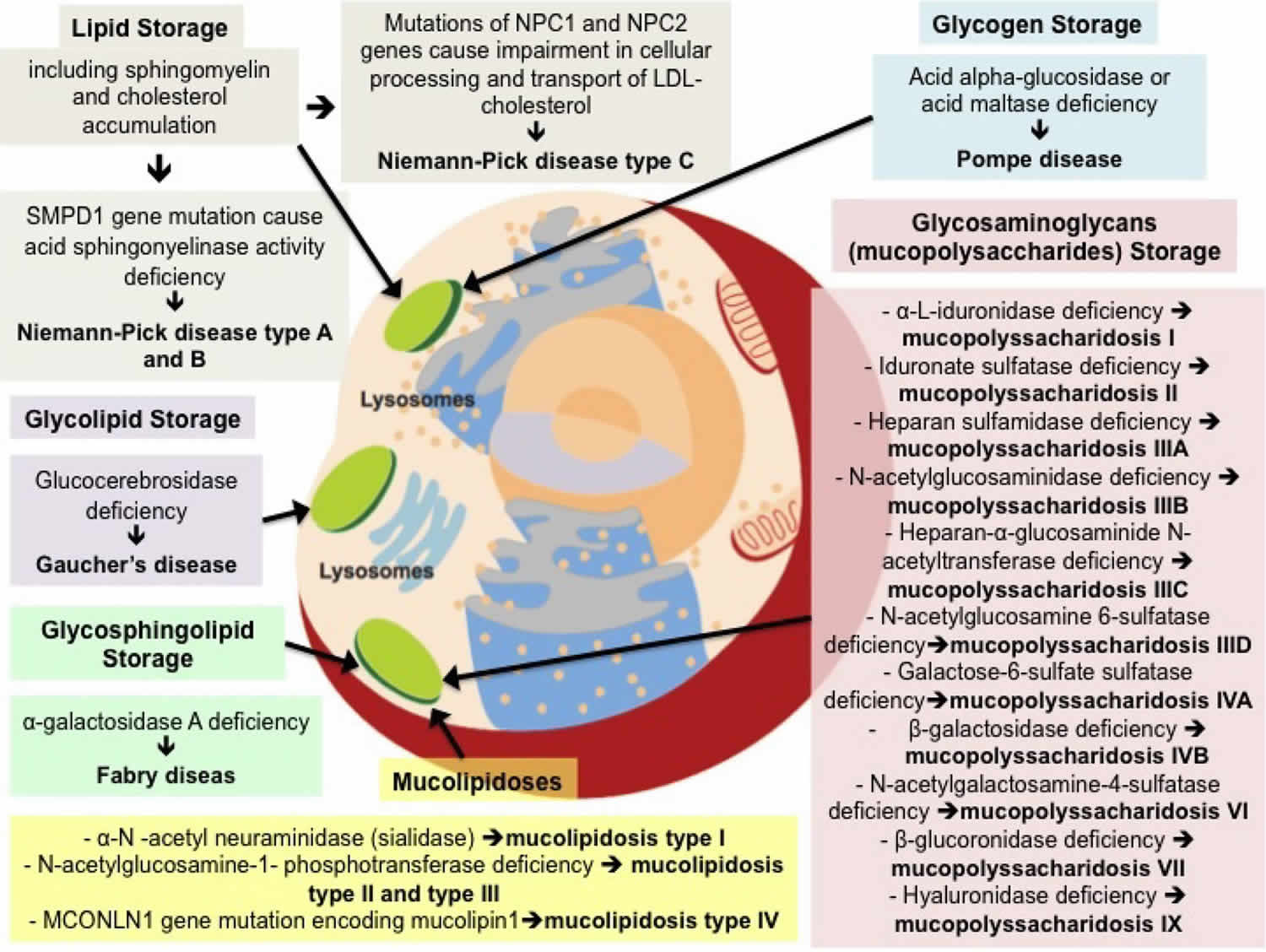
5 Classification of Lysosomal Storage Diseases Oncohema Key
Lysosome Biochemistry Medbullets Step 1
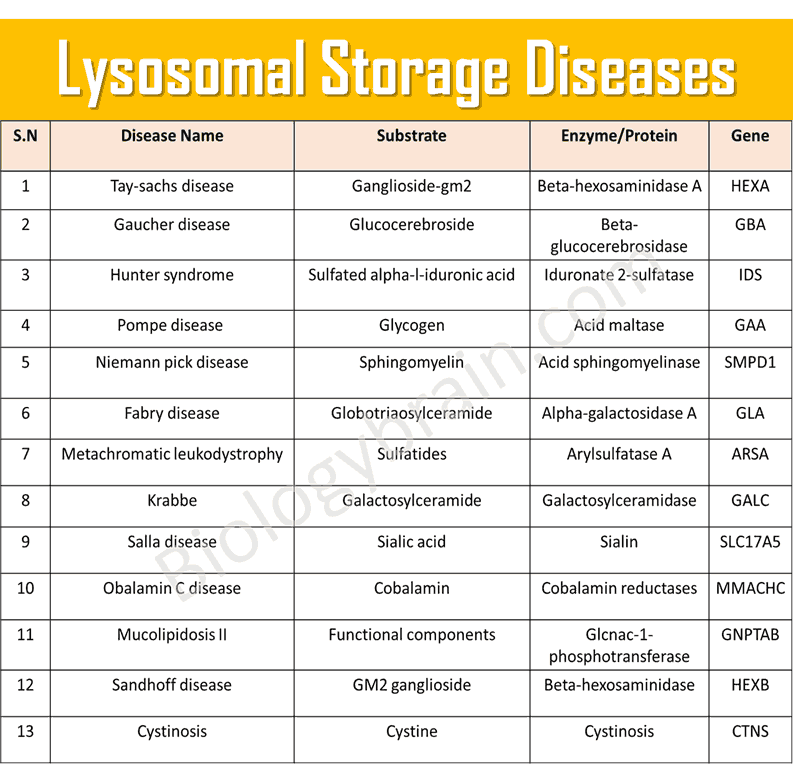
What are lysosomal storage diseases? Biology Brain
Lysosomal storage diseases The Clinical Advisor
5 Classification of Lysosomal Storage Diseases Oncohema Key
In This Review, We Interpreted The Key Biological Functions Of Lysosomes In Four Areas:
Long Known As Terminal Degradation Stations, Lysosomes Have Emerged As Sophisticated Signalling Centres That Govern Cell Growth, Division And Differentiation.
Here, We Summarize Current Knowledge Of The Regulatory Mechanisms Of Lysosome Biogenesis, Including Synthesis Of Lysosomal Proteins And Their Delivery Via The Endosome.
Related Post: