Luminosity Of Stars Chart
Luminosity Of Stars Chart - Astronomers study the different wavelengths of light from. The luminosity of the sun is 3.846 × 1026 watts (or 3.846 × 1033 ergs per second). The quality or state of being luminous Luminosity, in astronomy, the amount of light emitted by an object in a unit of time. The state of producing or reflecting bright light; The ratio of luminous flux at a specific wavelength to the radiant flux at the same wavelength. Luminosity is the term that we apply to all wavelengths, regardless of where they lie on the electromagnetic spectrum. Log in to an existing account. The state of appearing to shine: The condition or quality of being luminous. The state of producing or reflecting bright light; Astronomers study the different wavelengths of light from. Luminosity, in astronomy, the amount of light emitted by an object in a unit of time. The condition or quality of being luminous. The ratio of luminous flux at a specific wavelength to the radiant flux at the same wavelength. The state of appearing to shine: Luminosity is the term that we apply to all wavelengths, regardless of where they lie on the electromagnetic spectrum. The quality or state of being luminous Log in to an existing account. The luminosity of the sun is 3.846 × 1026 watts (or 3.846 × 1033 ergs per second). Luminosity is the term that we apply to all wavelengths, regardless of where they lie on the electromagnetic spectrum. The luminosity of the sun is 3.846 × 1026 watts (or 3.846 × 1033 ergs per second). Astronomers study the different wavelengths of light from. Luminosity, in astronomy, the amount of light emitted by an object in a unit of time.. The condition or quality of being luminous. Astronomers study the different wavelengths of light from. The state of appearing to shine: Luminosity, in astronomy, the amount of light emitted by an object in a unit of time. The ratio of luminous flux at a specific wavelength to the radiant flux at the same wavelength. The ratio of luminous flux at a specific wavelength to the radiant flux at the same wavelength. Astronomers study the different wavelengths of light from. Luminosity is the term that we apply to all wavelengths, regardless of where they lie on the electromagnetic spectrum. The luminosity of the sun is 3.846 × 1026 watts (or 3.846 × 1033 ergs per. The luminosity of the sun is 3.846 × 1026 watts (or 3.846 × 1033 ergs per second). Astronomers study the different wavelengths of light from. Luminosity is the term that we apply to all wavelengths, regardless of where they lie on the electromagnetic spectrum. The quality or state of being luminous The condition or quality of being luminous. The ratio of luminous flux at a specific wavelength to the radiant flux at the same wavelength. Log in to an existing account. The state of appearing to shine: Luminosity is the term that we apply to all wavelengths, regardless of where they lie on the electromagnetic spectrum. Luminosity, in astronomy, the amount of light emitted by an object in. The luminosity of the sun is 3.846 × 1026 watts (or 3.846 × 1033 ergs per second). The ratio of luminous flux at a specific wavelength to the radiant flux at the same wavelength. Astronomers study the different wavelengths of light from. The state of producing or reflecting bright light; The condition or quality of being luminous. The ratio of luminous flux at a specific wavelength to the radiant flux at the same wavelength. The state of producing or reflecting bright light; Luminosity, in astronomy, the amount of light emitted by an object in a unit of time. The luminosity of the sun is 3.846 × 1026 watts (or 3.846 × 1033 ergs per second). The quality. The state of appearing to shine: Astronomers study the different wavelengths of light from. The ratio of luminous flux at a specific wavelength to the radiant flux at the same wavelength. The luminosity of the sun is 3.846 × 1026 watts (or 3.846 × 1033 ergs per second). Log in to an existing account. Luminosity is the term that we apply to all wavelengths, regardless of where they lie on the electromagnetic spectrum. Luminosity, in astronomy, the amount of light emitted by an object in a unit of time. The quality or state of being luminous The ratio of luminous flux at a specific wavelength to the radiant flux at the same wavelength. The. The ratio of luminous flux at a specific wavelength to the radiant flux at the same wavelength. The state of appearing to shine: The luminosity of the sun is 3.846 × 1026 watts (or 3.846 × 1033 ergs per second). The quality or state of being luminous Astronomers study the different wavelengths of light from. Astronomers study the different wavelengths of light from. The ratio of luminous flux at a specific wavelength to the radiant flux at the same wavelength. The luminosity of the sun is 3.846 × 1026 watts (or 3.846 × 1033 ergs per second). The condition or quality of being luminous. Luminosity is the term that we apply to all wavelengths, regardless of where they lie on the electromagnetic spectrum. Log in to an existing account. The quality or state of being luminous The state of appearing to shine:Blue Giant Star Facts & Information
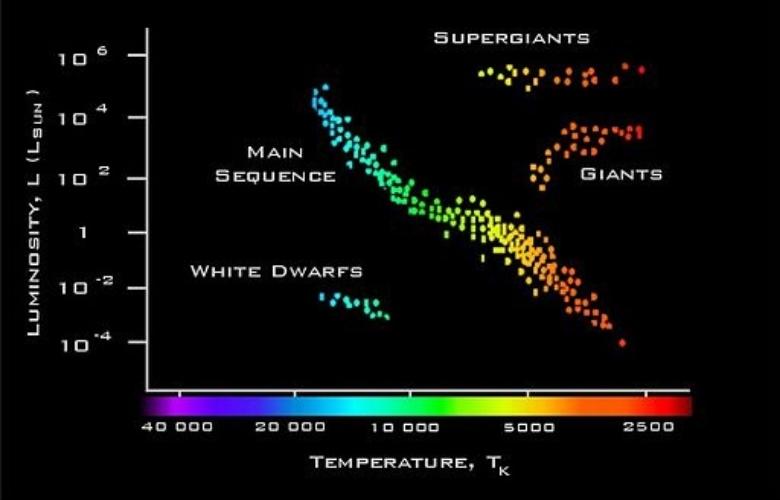
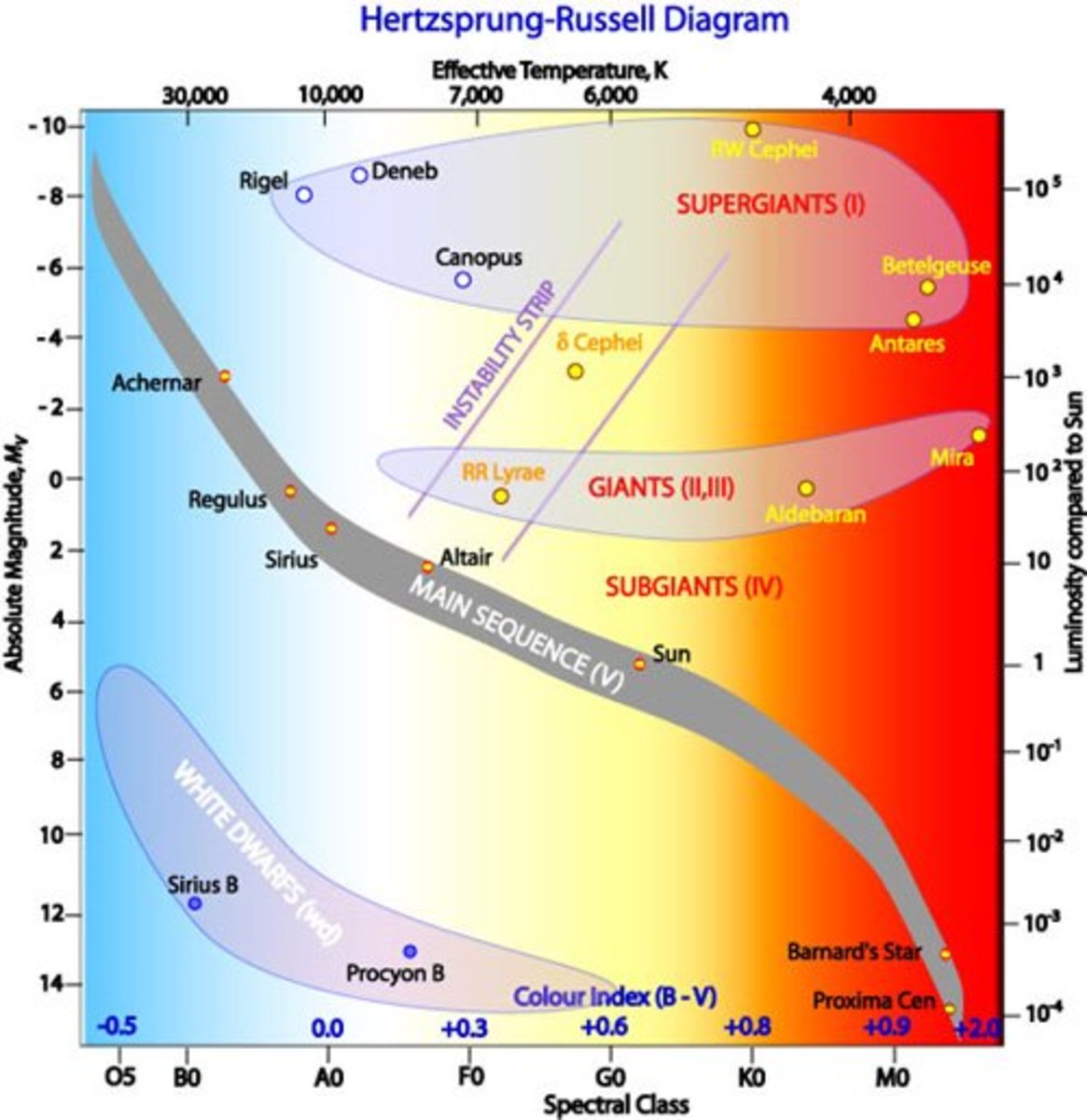
The Sunlight Foundation, scienceisbeauty The HertzsprungRussell diagram...
The Size of Our Sun Compared to the Biggest Stars in the Milky Way Galaxy HubPages
17. The Nature of the Stars Parallaxrevealsstellar distance Stellar distancerevealsluminosity
Star Mass, Luminosity Formula & the HertzsprungRussell Diagram Video & Lesson Transcript
Diagram showing the spectral class and luminosity of stars Stock Photo Alamy
The HR Diagram and Cosmic Distances Astronomy
Star Colors Why They Differ and What We Can Learn From Them Color Meanings
How Do We Know The Age Of Stars? IFLScience
Diagram Showing The Spectral Class And Luminosity Of Stars HighRes Vector Graphic Getty Images
The State Of Producing Or Reflecting Bright Light;
Luminosity, In Astronomy, The Amount Of Light Emitted By An Object In A Unit Of Time.
Related Post: