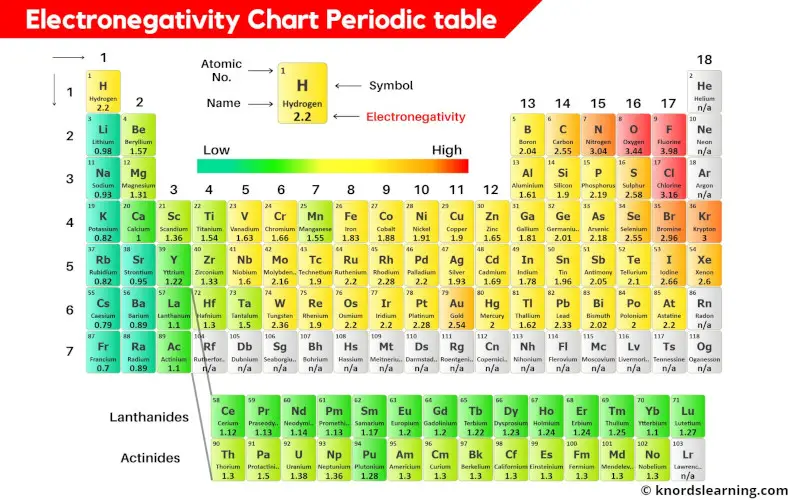
Electronegativity Periodic Table Chart
Electronegativity Periodic Table Chart - However, the difference in electronegativity between. 1 following is from wikipedia electronegativity, symbolized as χ, is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a. The trend in electronegativity can be seen on the periodic table and, more specifically, in the following graphs. See an electronegativity example, and discover how to find electronegativity using the right tools for. Noble gases are supposed to be happy with the amount of electrons they have, because they have 8 valence electrons (thus, most. Covalent bonds, and discover how to predict. Why do krypton and xenon have high electronegativity? I guess this electronegativity comes from a few aspects. In the 1930s, scientist linus pauling proposed a scale to measure and explain the attraction atoms have for valence electrons in bonds. The electronegativity difference serves as a measure of percentage at which a bond is ionic.roughly speaking, electro negativity difference of 1.7 is equivalent to 50 ℅ ionic. Trace ionic character trend on the periodic table, examine ionic vs. If we take the most simple definition, that it is the sum of the electron affinity and the ionization energy (divided by. 1 following is from wikipedia electronegativity, symbolized as χ, is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a. The trend in electronegativity can be seen on the periodic table and, more specifically, in the following graphs. Noble gases are supposed to be happy with the amount of electrons they have, because they have 8 valence electrons (thus, most. The electronegativity difference serves as a measure of percentage at which a bond is ionic.roughly speaking, electro negativity difference of 1.7 is equivalent to 50 ℅ ionic. Covalent bonds, and discover how to predict. Why do krypton and xenon have high electronegativity? Learn what ionic character is. In this sense, elements are less electronegative (or more electropositive) as you go down any group in the periodic table. The electronegativity difference serves as a measure of percentage at which a bond is ionic.roughly speaking, electro negativity difference of 1.7 is equivalent to 50 ℅ ionic. Trace ionic character trend on the periodic table, examine ionic vs. 1 following is from wikipedia electronegativity, symbolized as χ, is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract. In this sense, elements are less electronegative (or more electropositive) as you go down any group in the periodic table. Covalent bonds, and discover how to predict. Learn what ionic character is. In the 1930s, scientist linus pauling proposed a scale to measure and explain the attraction atoms have for valence electrons in bonds. The electronegativity difference serves as a. Noble gases are supposed to be happy with the amount of electrons they have, because they have 8 valence electrons (thus, most. The trend in electronegativity can be seen on the periodic table and, more specifically, in the following graphs. In the 1930s, scientist linus pauling proposed a scale to measure and explain the attraction atoms have for valence electrons. If we take the most simple definition, that it is the sum of the electron affinity and the ionization energy (divided by. I guess this electronegativity comes from a few aspects. However, the difference in electronegativity between. Learn what ionic character is. The trend in electronegativity can be seen on the periodic table and, more specifically, in the following graphs. Electronegativity increases across a period In the 1930s, scientist linus pauling proposed a scale to measure and explain the attraction atoms have for valence electrons in bonds. The electronegativity difference serves as a measure of percentage at which a bond is ionic.roughly speaking, electro negativity difference of 1.7 is equivalent to 50 ℅ ionic. Learn what ionic character is. In. Why do krypton and xenon have high electronegativity? The electronegativity difference serves as a measure of percentage at which a bond is ionic.roughly speaking, electro negativity difference of 1.7 is equivalent to 50 ℅ ionic. Covalent bonds, and discover how to predict. In the 1930s, scientist linus pauling proposed a scale to measure and explain the attraction atoms have for. If we take the most simple definition, that it is the sum of the electron affinity and the ionization energy (divided by. In the 1930s, scientist linus pauling proposed a scale to measure and explain the attraction atoms have for valence electrons in bonds. The trend in electronegativity can be seen on the periodic table and, more specifically, in the. See an electronegativity example, and discover how to find electronegativity using the right tools for. The trend in electronegativity can be seen on the periodic table and, more specifically, in the following graphs. However, the difference in electronegativity between. Learn what ionic character is. In the 1930s, scientist linus pauling proposed a scale to measure and explain the attraction atoms. Electronegativity increases across a period However, the difference in electronegativity between. Learn what ionic character is. Trace ionic character trend on the periodic table, examine ionic vs. I guess this electronegativity comes from a few aspects. Why do krypton and xenon have high electronegativity? The trend in electronegativity can be seen on the periodic table and, more specifically, in the following graphs. In the 1930s, scientist linus pauling proposed a scale to measure and explain the attraction atoms have for valence electrons in bonds. Noble gases are supposed to be happy with the amount of electrons. The electronegativity difference serves as a measure of percentage at which a bond is ionic.roughly speaking, electro negativity difference of 1.7 is equivalent to 50 ℅ ionic. If we take the most simple definition, that it is the sum of the electron affinity and the ionization energy (divided by. Learn what ionic character is. Trace ionic character trend on the periodic table, examine ionic vs. See an electronegativity example, and discover how to find electronegativity using the right tools for. Noble gases are supposed to be happy with the amount of electrons they have, because they have 8 valence electrons (thus, most. I guess this electronegativity comes from a few aspects. In the 1930s, scientist linus pauling proposed a scale to measure and explain the attraction atoms have for valence electrons in bonds. Electronegativity increases across a period However, the difference in electronegativity between. 1 following is from wikipedia electronegativity, symbolized as χ, is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a. In this sense, elements are less electronegative (or more electropositive) as you go down any group in the periodic table.Periodic table with Electronegativity Values (Labeled Image)
Electronegativity Chart Printable periodic table of the elements
Printable Periodic Table With Electronegativity Printable Calendars AT A GLANCE
Electronegativity Table Easy Hard Science
Periodic Table of Electronegativities
Electronegativity Definition, Value Chart, and Trend in Periodic Table
Electronegativity Chart of all Elements (With Periodic table)
Electronegativity Chart Printable periodic table of the elements
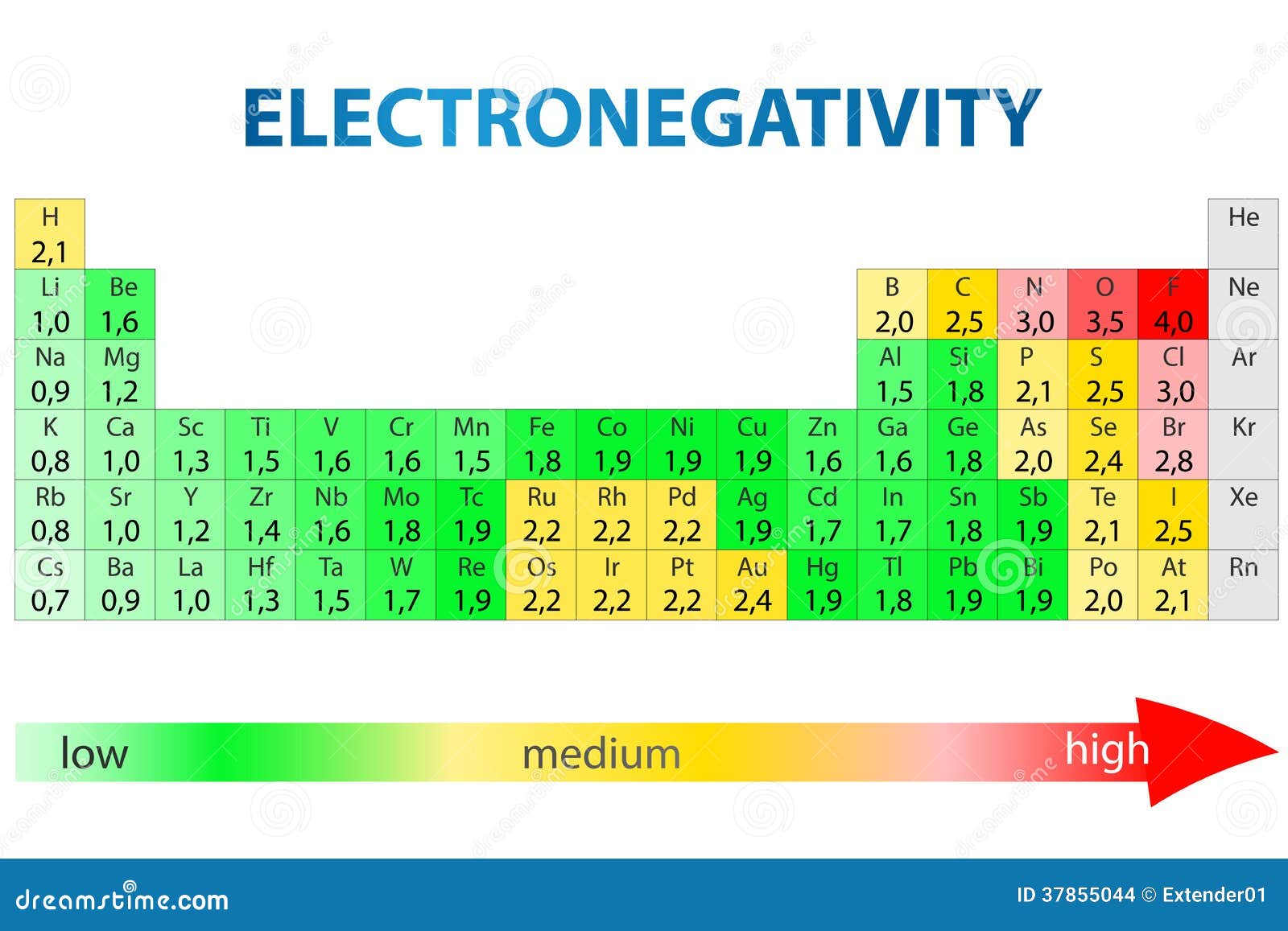
Electronegativity Periodic Table Stock Photo Image of elements, electrons 37855044
Electronegativity Definition, Value Chart, and Trend in Periodic Table
The Trend In Electronegativity Can Be Seen On The Periodic Table And, More Specifically, In The Following Graphs.
Covalent Bonds, And Discover How To Predict.
Why Do Krypton And Xenon Have High Electronegativity?
Related Post:
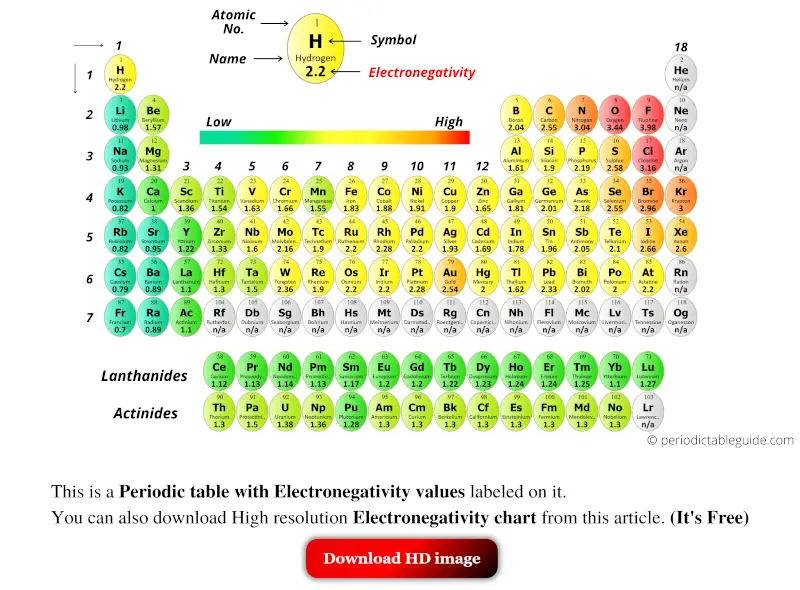
/PeriodicTableEnegativity-56a12c955f9b58b7d0bcc69d.png)


.PNG)