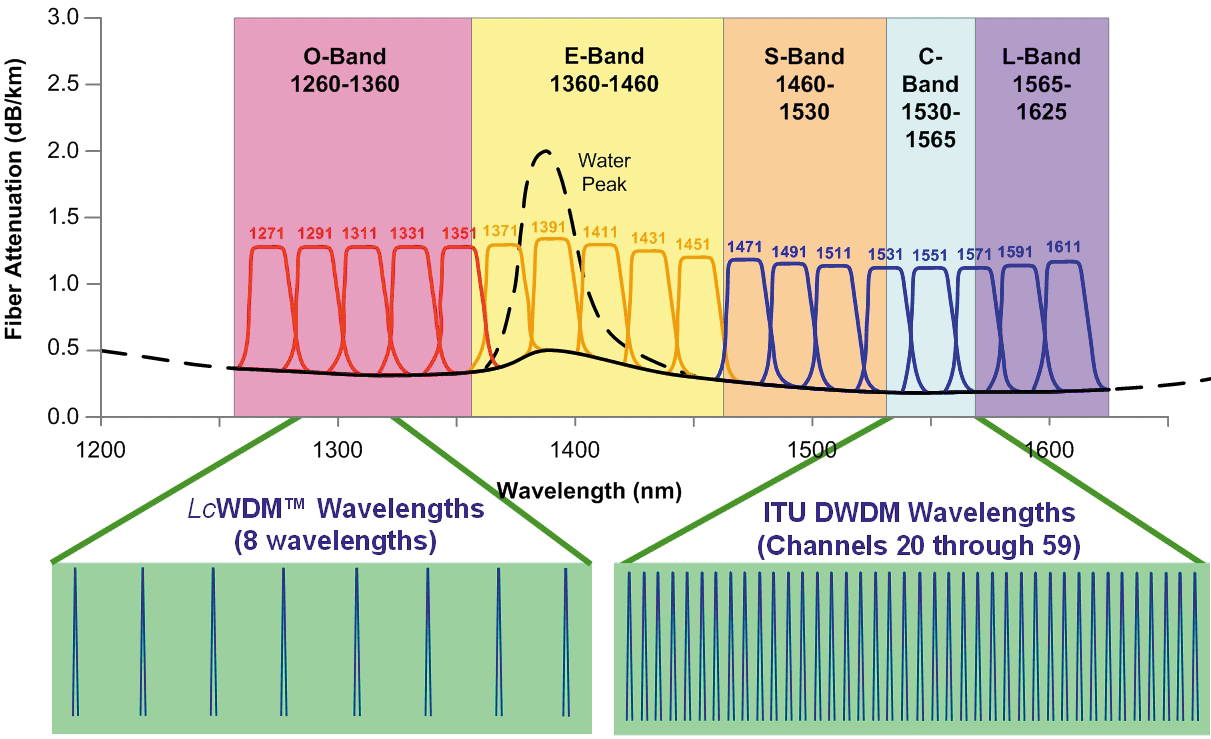
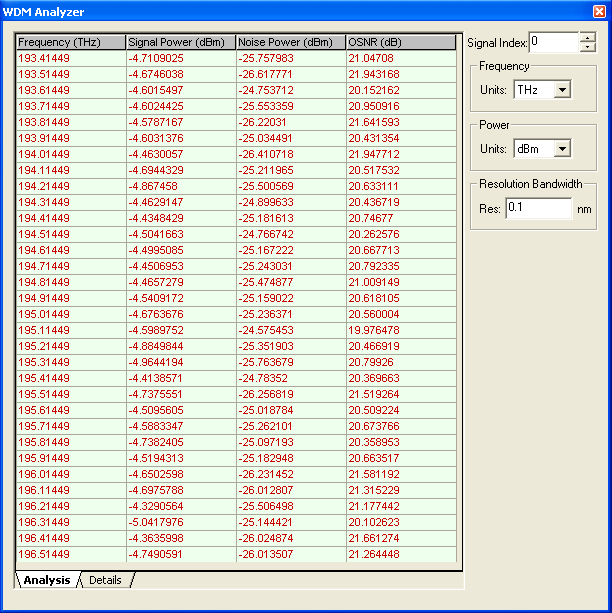
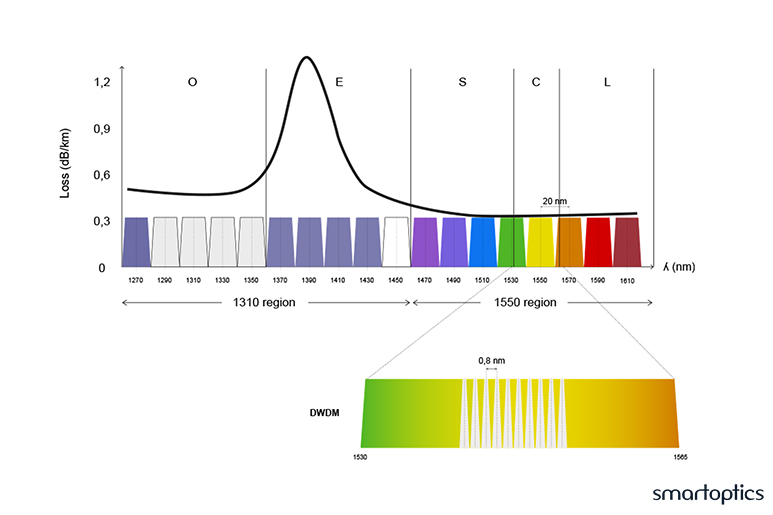
Dwdm Wavelengths Chart
Dwdm Wavelengths Chart - Dwdm works by combining and transmitting. Dwdm is defined in terms of frequencies. Wdm systems are divided into three different wavelength patterns: Dwdm refers to dense wavelength division multiplexing. Dwdm’s tighter wavelength spacing fits more channels onto a single fiber, but costs more to implement and operate. Normal wdm (sometimes called bwdm) uses the two normal. The technology supports multiplexed transmission of multiple optical wavelengths in a single fiber. Dense wavelength division multiplexing (dwdm) is a fiber optics technology for connecting multiple channels over a dark fiber pair using a multiplexer. Normal (wdm), coarse (cwdm) and dense (dwdm). The technology supports multiplexed transmission of multiple optical wavelengths in a single fiber. Dwdm refers to dense wavelength division multiplexing. Wdm systems are divided into three different wavelength patterns: Dwdm’s tighter wavelength spacing fits more channels onto a single fiber, but costs more to implement and operate. Dense wavelength division multiplexing (dwdm) is a fiber optics technology for connecting multiple channels over a dark fiber pair using a multiplexer. Dwdm works by combining and transmitting. Normal (wdm), coarse (cwdm) and dense (dwdm). Dwdm is defined in terms of frequencies. Normal wdm (sometimes called bwdm) uses the two normal. Dwdm refers to dense wavelength division multiplexing. The technology supports multiplexed transmission of multiple optical wavelengths in a single fiber. Dense wavelength division multiplexing (dwdm) is a fiber optics technology for connecting multiple channels over a dark fiber pair using a multiplexer. Dwdm is defined in terms of frequencies. Wdm systems are divided into three different wavelength patterns: Wdm systems are divided into three different wavelength patterns: Dwdm works by combining and transmitting. Dense wavelength division multiplexing (dwdm) is a fiber optics technology for connecting multiple channels over a dark fiber pair using a multiplexer. Dwdm is defined in terms of frequencies. Normal wdm (sometimes called bwdm) uses the two normal. Wdm systems are divided into three different wavelength patterns: The technology supports multiplexed transmission of multiple optical wavelengths in a single fiber. Dense wavelength division multiplexing (dwdm) is a fiber optics technology for connecting multiple channels over a dark fiber pair using a multiplexer. Dwdm’s tighter wavelength spacing fits more channels onto a single fiber, but costs more to implement. Wdm systems are divided into three different wavelength patterns: The technology supports multiplexed transmission of multiple optical wavelengths in a single fiber. Normal wdm (sometimes called bwdm) uses the two normal. Dwdm’s tighter wavelength spacing fits more channels onto a single fiber, but costs more to implement and operate. Dense wavelength division multiplexing (dwdm) is a fiber optics technology for. Dwdm works by combining and transmitting. Dwdm is defined in terms of frequencies. Dwdm refers to dense wavelength division multiplexing. Dwdm’s tighter wavelength spacing fits more channels onto a single fiber, but costs more to implement and operate. Wdm systems are divided into three different wavelength patterns: Normal (wdm), coarse (cwdm) and dense (dwdm). The technology supports multiplexed transmission of multiple optical wavelengths in a single fiber. Dwdm’s tighter wavelength spacing fits more channels onto a single fiber, but costs more to implement and operate. Dense wavelength division multiplexing (dwdm) is a fiber optics technology for connecting multiple channels over a dark fiber pair using a multiplexer.. Normal (wdm), coarse (cwdm) and dense (dwdm). Dwdm is defined in terms of frequencies. Dense wavelength division multiplexing (dwdm) is a fiber optics technology for connecting multiple channels over a dark fiber pair using a multiplexer. Dwdm’s tighter wavelength spacing fits more channels onto a single fiber, but costs more to implement and operate. Dwdm works by combining and transmitting. Wdm systems are divided into three different wavelength patterns: Dwdm works by combining and transmitting. Normal wdm (sometimes called bwdm) uses the two normal. The technology supports multiplexed transmission of multiple optical wavelengths in a single fiber. Dwdm is defined in terms of frequencies. Wdm systems are divided into three different wavelength patterns: Dwdm is defined in terms of frequencies. Dwdm refers to dense wavelength division multiplexing. Dwdm works by combining and transmitting. The technology supports multiplexed transmission of multiple optical wavelengths in a single fiber. Dwdm is defined in terms of frequencies. Normal (wdm), coarse (cwdm) and dense (dwdm). Dwdm works by combining and transmitting. The technology supports multiplexed transmission of multiple optical wavelengths in a single fiber. Wdm systems are divided into three different wavelength patterns: Dwdm refers to dense wavelength division multiplexing. Normal (wdm), coarse (cwdm) and dense (dwdm). Dwdm works by combining and transmitting. Wdm systems are divided into three different wavelength patterns: Normal wdm (sometimes called bwdm) uses the two normal. Dense wavelength division multiplexing (dwdm) is a fiber optics technology for connecting multiple channels over a dark fiber pair using a multiplexer. Dwdm’s tighter wavelength spacing fits more channels onto a single fiber, but costs more to implement and operate.WDM Everything you Need to Know Precision OT
Optical Multiplexing & WDM Resource Guide
PPT Understanding DWDM PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6572025
CWDM or DWDM Which Should You Use and When? WWT
PPT DWDM Presentation PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID7348584
Dwdm Channel Wavelength Chart Ponasa
FiberOptics IP & FiberOptics Solutions
Information on Wavelengths, Frequencies and Channel Numbers, C/DWDM Fiberworks
DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing)
CWDM and DWDM explained
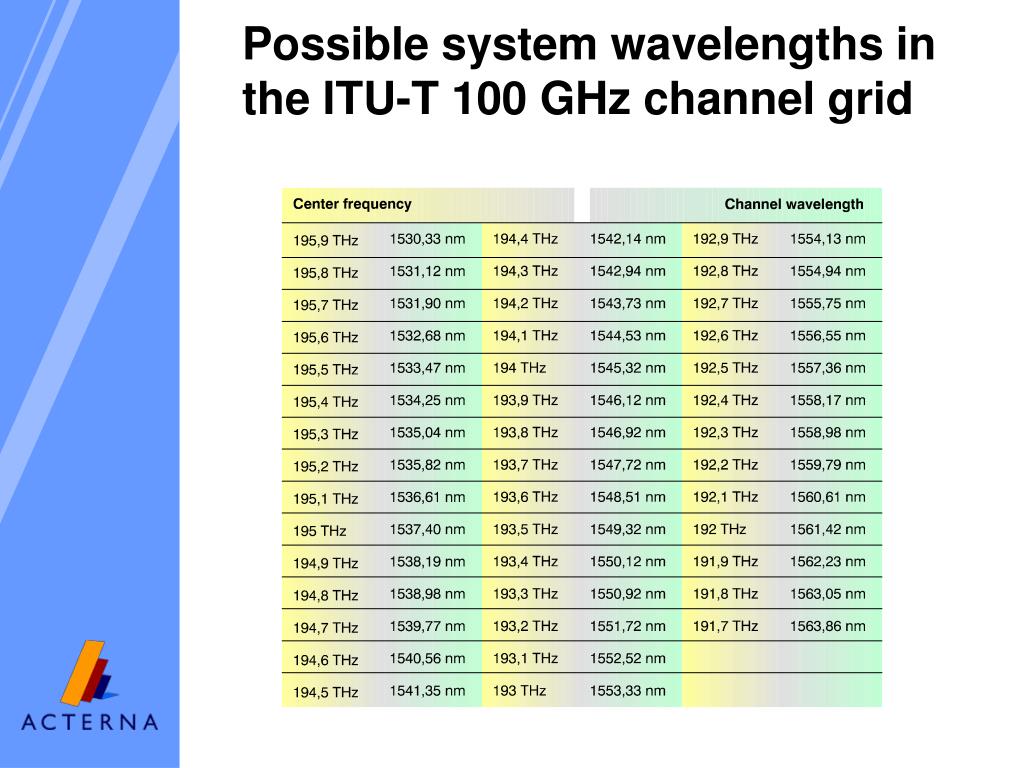
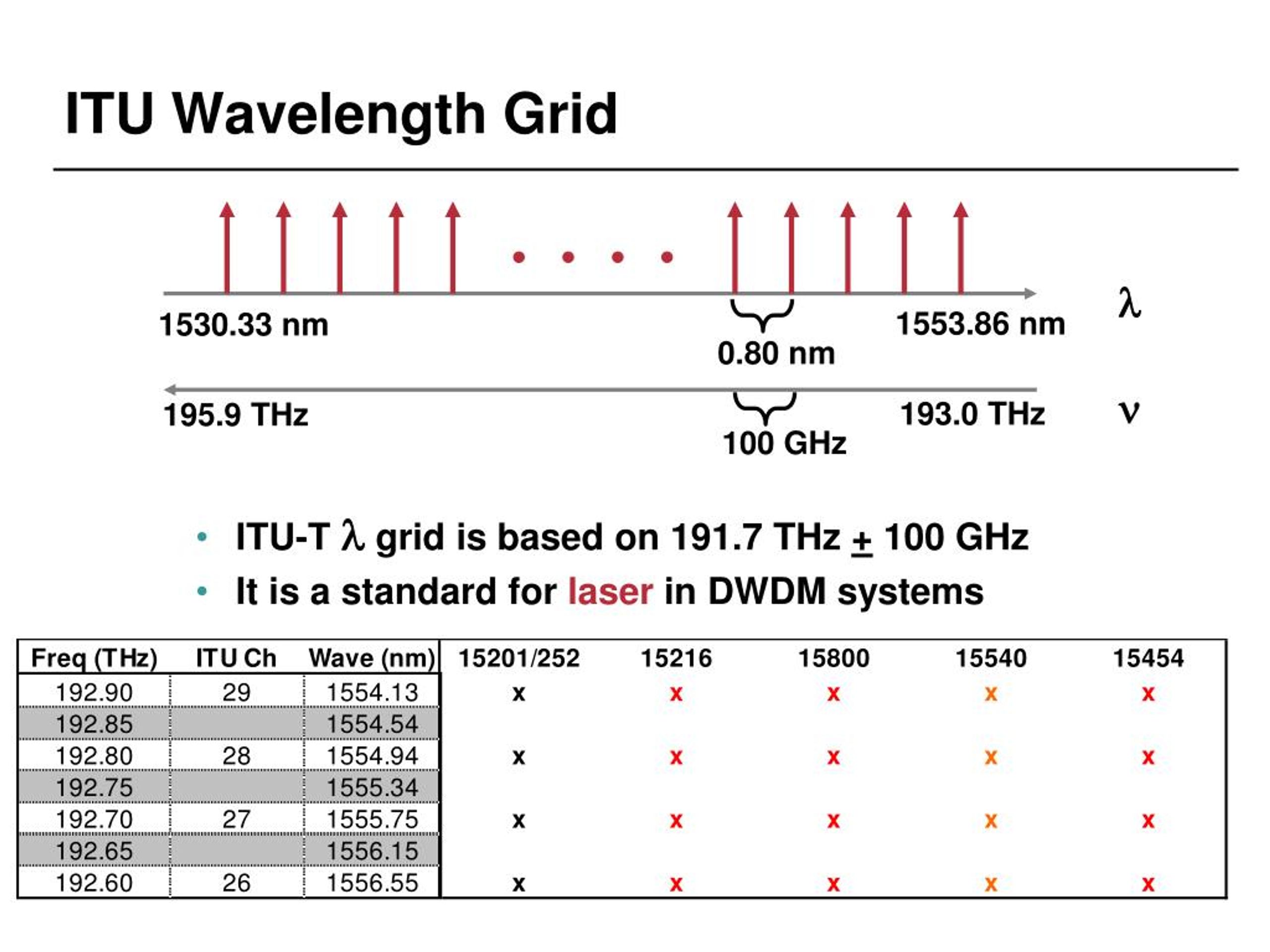
Dwdm Is Defined In Terms Of Frequencies.
The Technology Supports Multiplexed Transmission Of Multiple Optical Wavelengths In A Single Fiber.
Related Post:
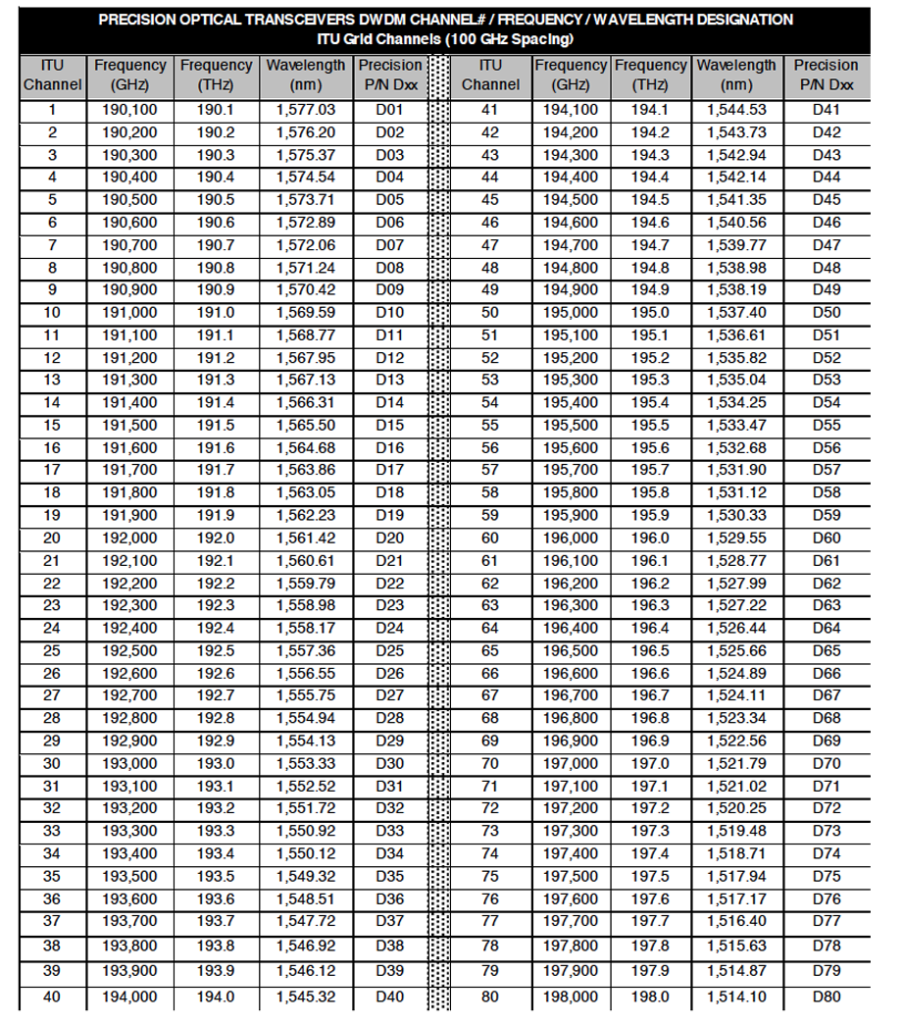

+l0+l1+ln+l+nm+nm.jpg)