Dielectric Corrosion Chart
Dielectric Corrosion Chart - Do metals have an infinite permittivity? These dipoles will create a field that opposes the external field, resulting. The author chooses a surface such that the. Dielectric materials tend to be more insulating than air, and thus by using such a material the plates (in a parallel plate capacitor) can be placed closer together which would. More polarization means more charge stored, so. Under the influence of an external electric field the dipoles in a dielectric medium arrange themselves. A dielectric with high permittivity ε ε permits (requires) more polarization for a given field magnitude than a low permittivity one. This is an example from the book. It is a function of state variables, electric field, frequency, temperature, pressure, mechanical stress, etc. I'm studying polarization, but i don't understand how i can solve the gauss's law for vector d. A dielectric with high permittivity ε ε permits (requires) more polarization for a given field magnitude than a low permittivity one. Do metals have an infinite permittivity? Dielectric materials tend to be more insulating than air, and thus by using such a material the plates (in a parallel plate capacitor) can be placed closer together which would. Bandgaps, as such, only exist in perfect crystals. The author chooses a surface such that the. More polarization means more charge stored, so. Because of this the value listed in a data sheet. The dielectric is a very polar, protic solvent, presumably water. With no dielectric material (only vacuum) between the plates, the capacitor is actually easier to explain: (few other solvents dissolve ions, polar aprotic almost never, exept ion pairs, but this is a different story) the dielectric constant. Because of this the value listed in a data sheet. This is higher than, say, glass. More polarization means more charge stored, so. Dielectric constant is a complex number. This is an example from the book. Do metals have an infinite permittivity? A dielectric with high permittivity ε ε permits (requires) more polarization for a given field magnitude than a low permittivity one. Under the influence of an external electric field the dipoles in a dielectric medium arrange themselves. More polarization means more charge stored, so. Dielectric materials tend to be more insulating than air, and. It is a function of state variables, electric field, frequency, temperature, pressure, mechanical stress, etc. Attach a voltage source (i.e., battery) to the capacitor. The author chooses a surface such that the. This is higher than, say, glass. Under the influence of an external electric field the dipoles in a dielectric medium arrange themselves. Because of this the value listed in a data sheet. Do metals have an infinite permittivity? With no dielectric material (only vacuum) between the plates, the capacitor is actually easier to explain: These dipoles will create a field that opposes the external field, resulting. This is higher than, say, glass. With no dielectric material (only vacuum) between the plates, the capacitor is actually easier to explain: Bandgaps, as such, only exist in perfect crystals. Under the influence of an external electric field the dipoles in a dielectric medium arrange themselves. More polarization means more charge stored, so. Attach a voltage source (i.e., battery) to the capacitor. A dielectric with high permittivity ε ε permits (requires) more polarization for a given field magnitude than a low permittivity one. The author chooses a surface such that the. It is a function of state variables, electric field, frequency, temperature, pressure, mechanical stress, etc. I'm studying polarization, but i don't understand how i can solve the gauss's law for vector. I'm studying polarization, but i don't understand how i can solve the gauss's law for vector d. These dipoles will create a field that opposes the external field, resulting. The dielectric is a very polar, protic solvent, presumably water. Attach a voltage source (i.e., battery) to the capacitor. It is a function of state variables, electric field, frequency, temperature, pressure,. (few other solvents dissolve ions, polar aprotic almost never, exept ion pairs, but this is a different story) the dielectric constant. Attach a voltage source (i.e., battery) to the capacitor. This is an example from the book. This is higher than, say, glass. Do metals have an infinite permittivity? The dielectric is a very polar, protic solvent, presumably water. These dipoles will create a field that opposes the external field, resulting. The author chooses a surface such that the. A dielectric with high permittivity ε ε permits (requires) more polarization for a given field magnitude than a low permittivity one. Dielectric materials tend to be more insulating than air,. I'm studying polarization, but i don't understand how i can solve the gauss's law for vector d. With no dielectric material (only vacuum) between the plates, the capacitor is actually easier to explain: Do metals have an infinite permittivity? Bandgaps, as such, only exist in perfect crystals. (few other solvents dissolve ions, polar aprotic almost never, exept ion pairs, but. It is a function of state variables, electric field, frequency, temperature, pressure, mechanical stress, etc. I'm studying polarization, but i don't understand how i can solve the gauss's law for vector d. The dielectric is a very polar, protic solvent, presumably water. Bandgaps, as such, only exist in perfect crystals. Because of this the value listed in a data sheet. This is an example from the book. Attach a voltage source (i.e., battery) to the capacitor. A dielectric with high permittivity ε ε permits (requires) more polarization for a given field magnitude than a low permittivity one. More polarization means more charge stored, so. (few other solvents dissolve ions, polar aprotic almost never, exept ion pairs, but this is a different story) the dielectric constant. Dielectric materials tend to be more insulating than air, and thus by using such a material the plates (in a parallel plate capacitor) can be placed closer together which would. Under the influence of an external electric field the dipoles in a dielectric medium arrange themselves. Do metals have an infinite permittivity? These dipoles will create a field that opposes the external field, resulting.Dielectric Corrosion Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
Dielectric Corrosion Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
Dielectric Corrosion Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
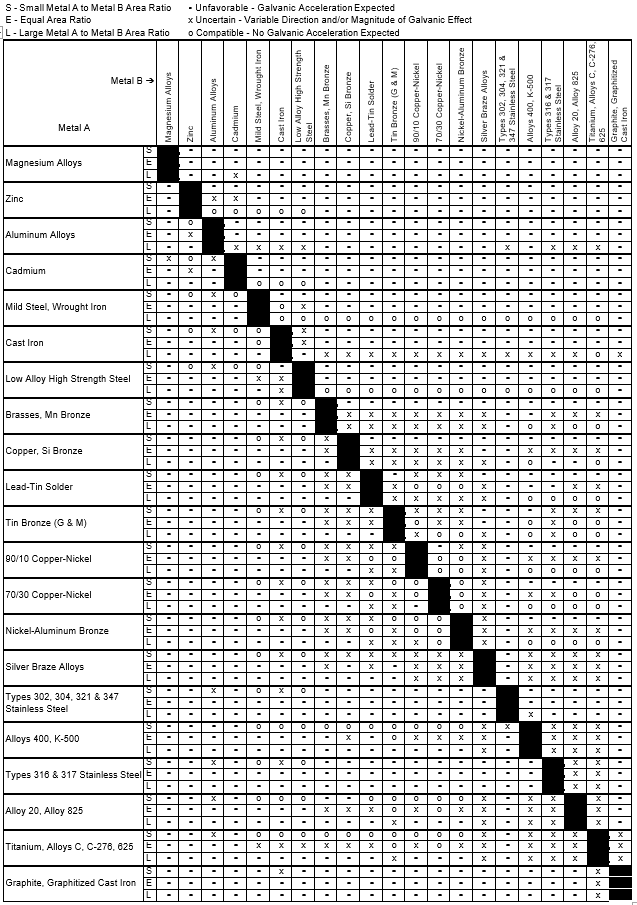
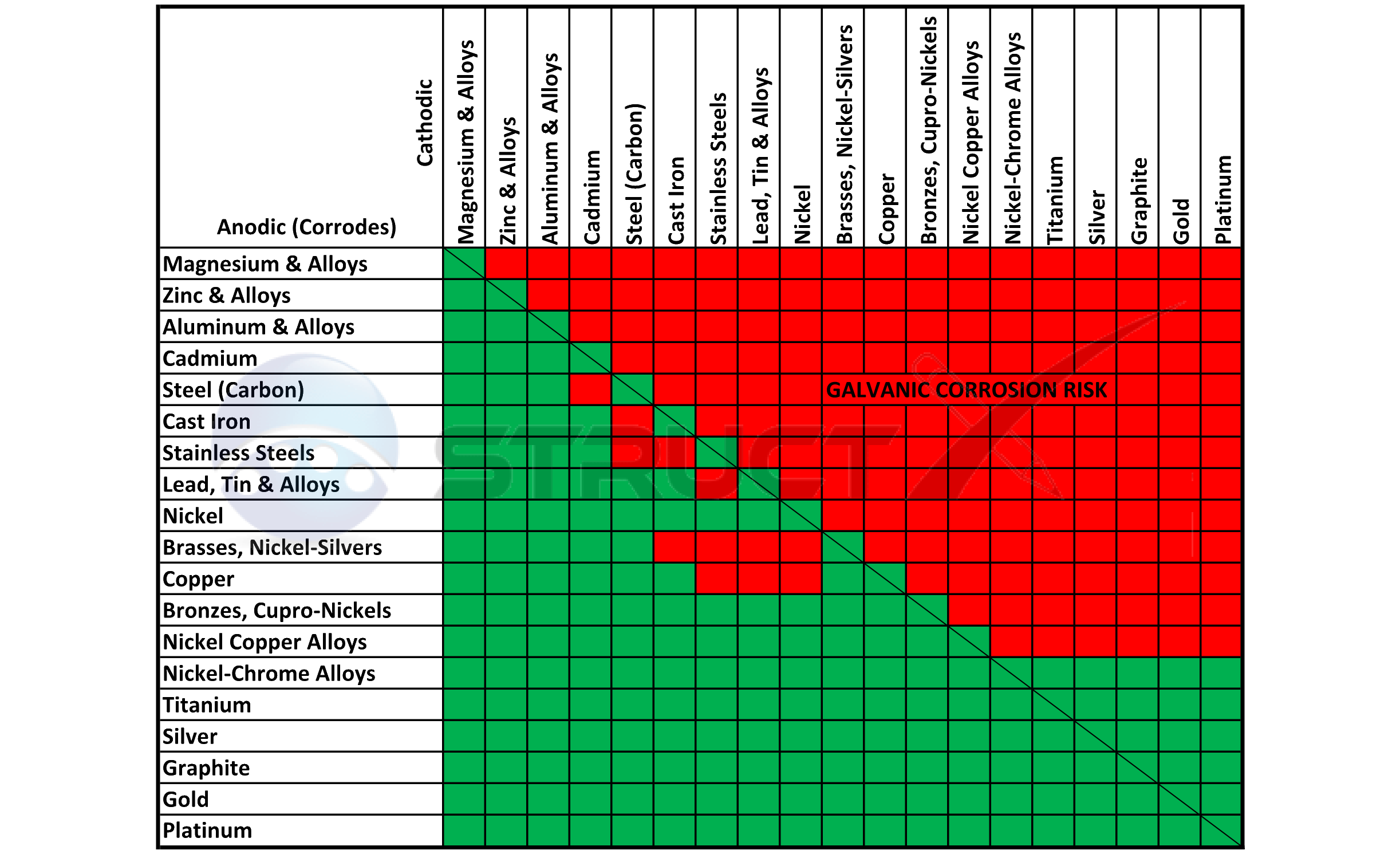
Galvanic Corrosion Chart
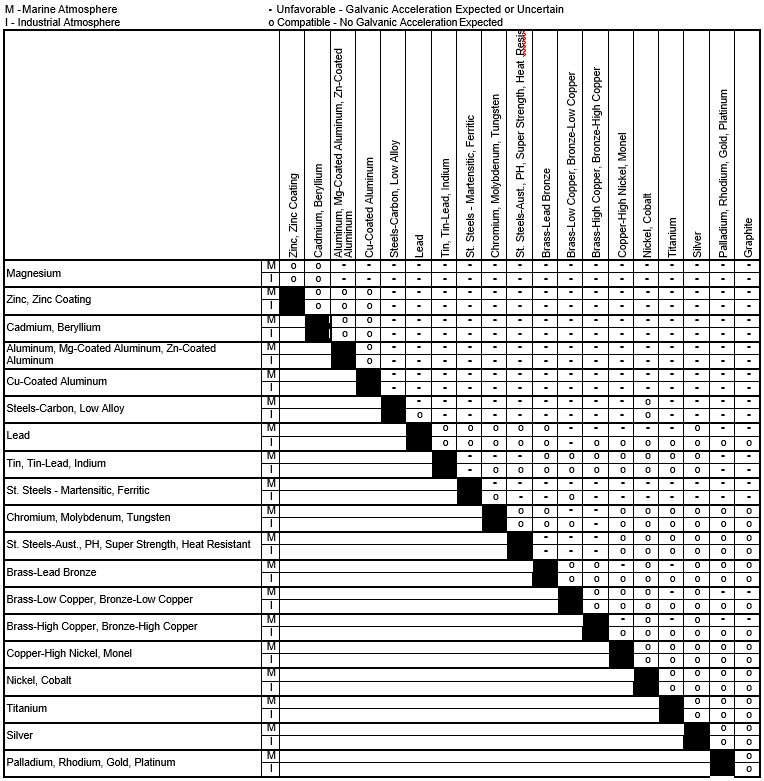
Galvanic Corrosion SSINA
Galvanic Action Chart
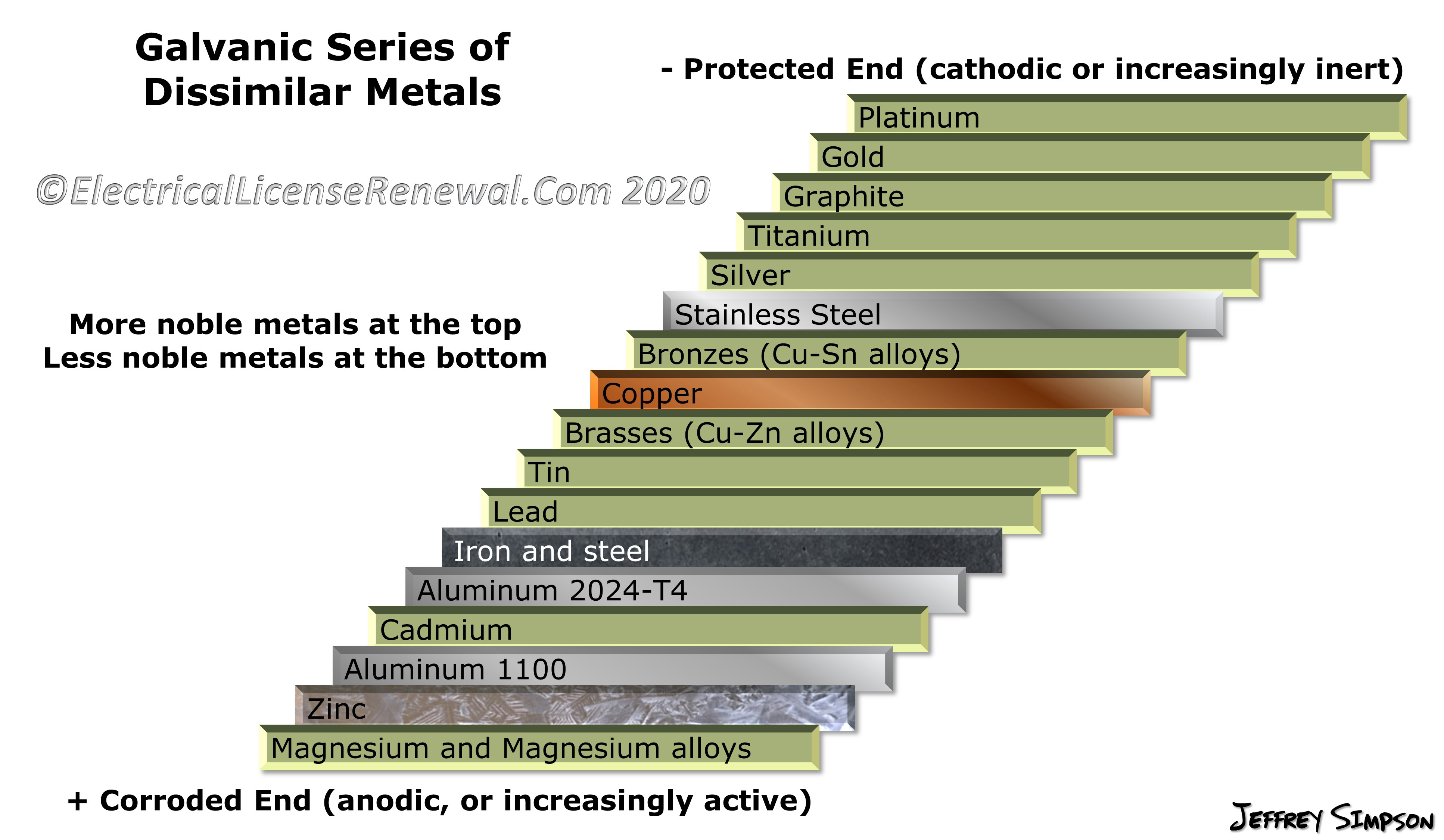
Galvanic Series
Galvanic Series (electrochemical series)
Dielectric Corrosion Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
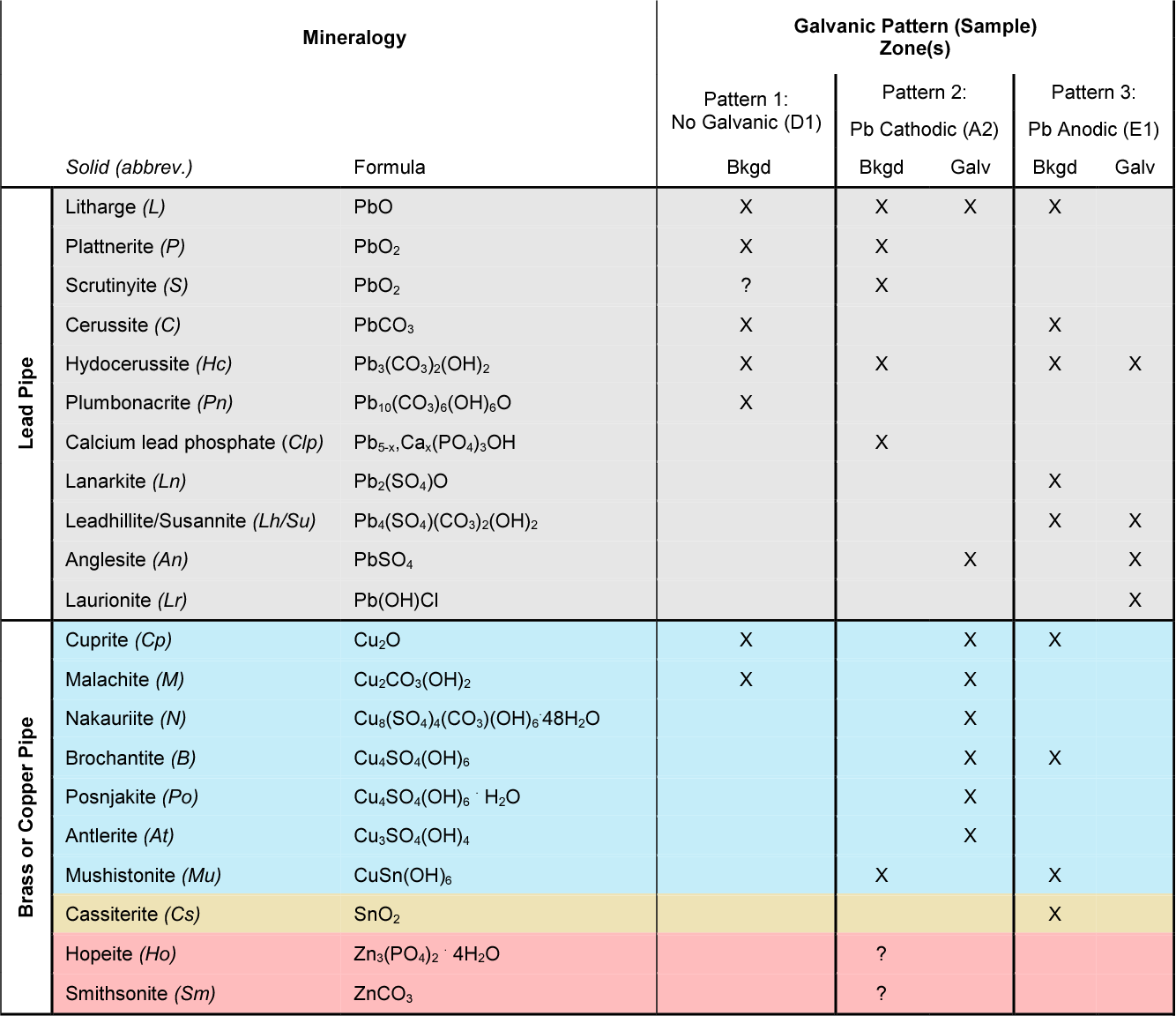
Inconel Galvanic Corrosion Chart
Dielectric Constant Is A Complex Number.
With No Dielectric Material (Only Vacuum) Between The Plates, The Capacitor Is Actually Easier To Explain:
This Is Higher Than, Say, Glass.
The Author Chooses A Surface Such That The.
Related Post: