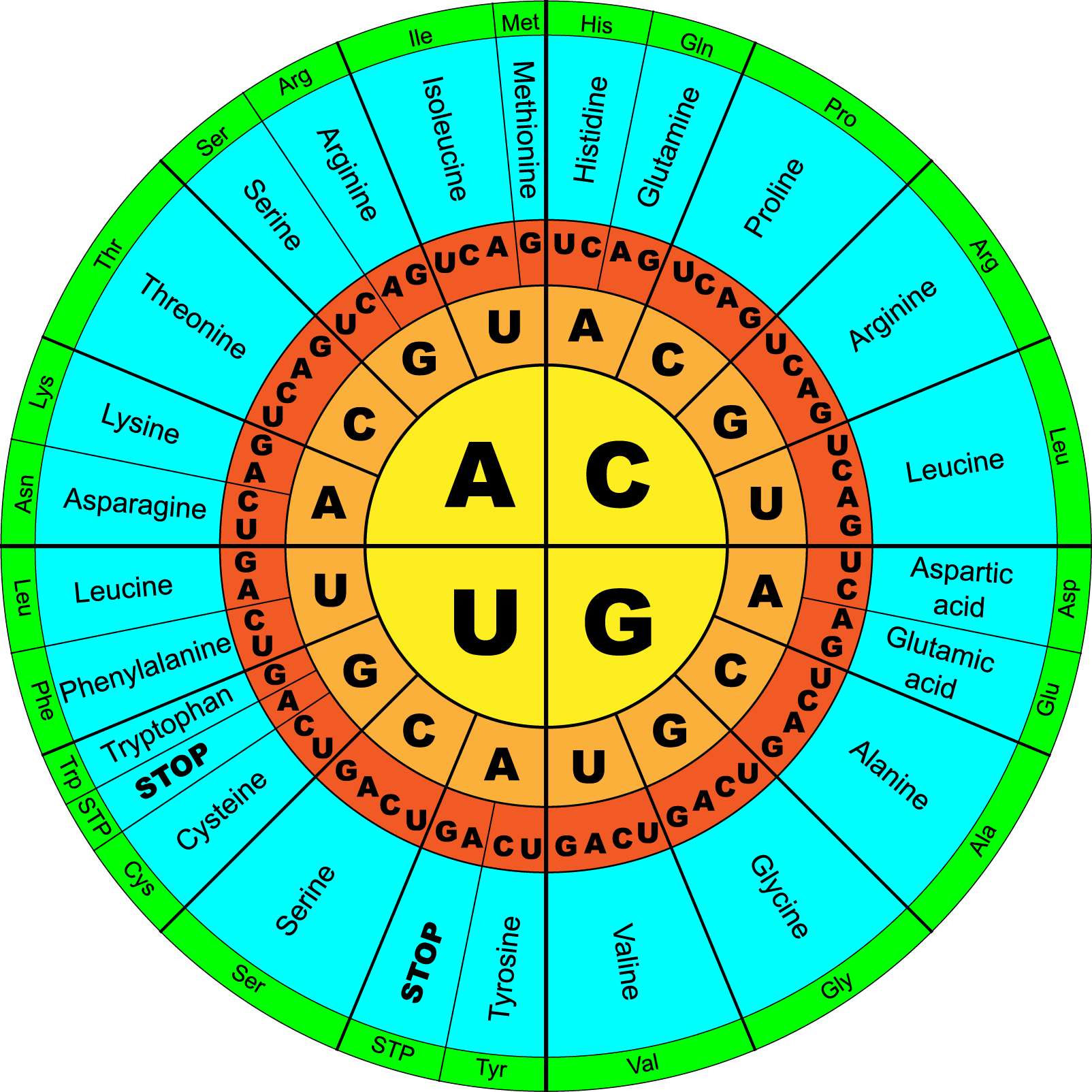
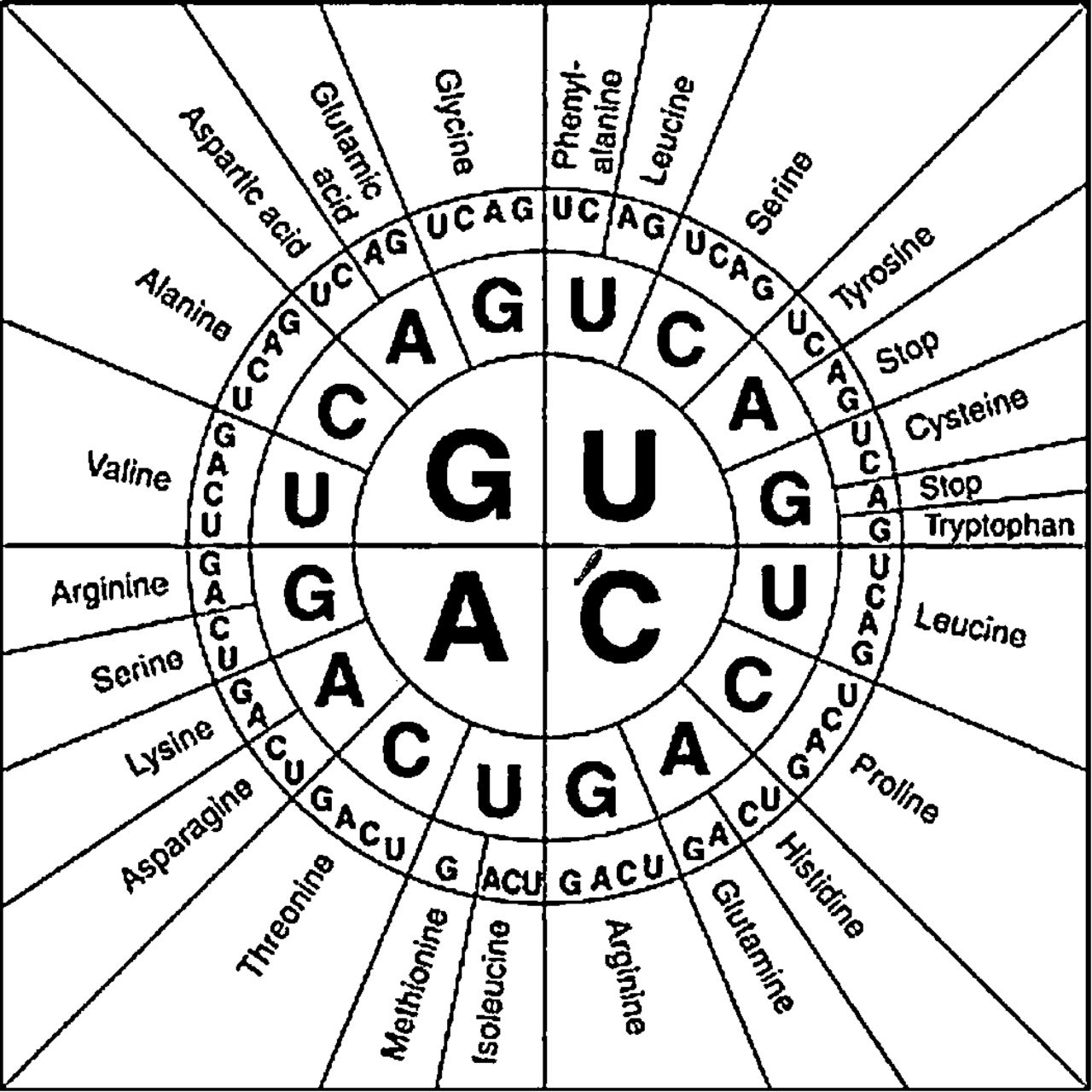
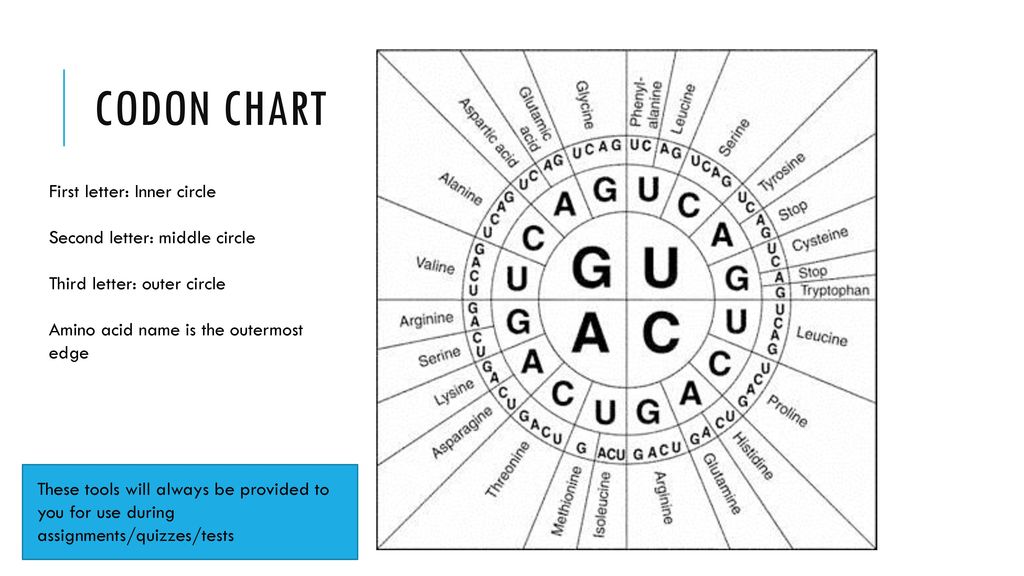
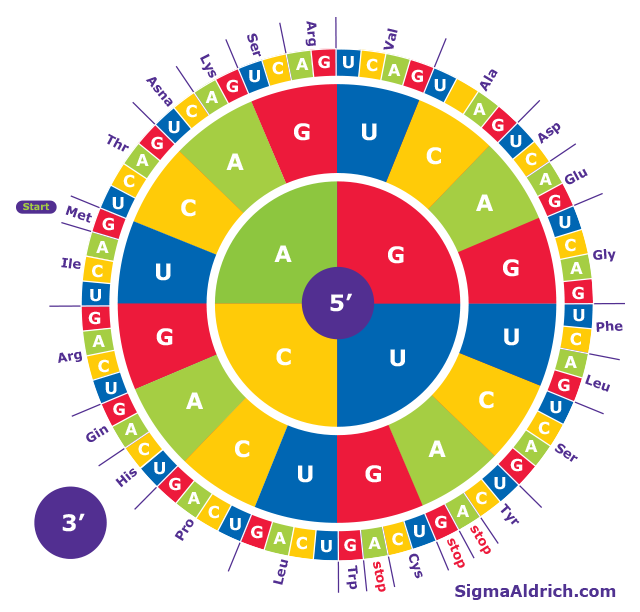
Circle Codon Chart
Circle Codon Chart - The set of all points on a plane that are at a fixed distance from a center. The area of a circle is π times the radius squared, which is written: A circle is also termed as the locus of the points drawn at an. The set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a fixed point, defined as the center, is called a circle. Circle worksheets, videos, tutorials and formulas involving arcs, chords, area, angles, secants and more. The distance from the center is called the radius, and the point is called the center. In case of a circle, it is much easier since we only need its radius or diameter to describe its geometry. Then, what are the radius and diameter of a circle? A few things around us that. A = π r 2. A circle is the set of points in a plane that are equidistant from a given point. The distance from the center is called the radius, and the point is called the center. The circle above is called circle o. In case of a circle, it is much easier since we only need its radius or diameter to describe its geometry. The area of a circle is π times the radius squared, which is written: Let us learn more about the circle definition, the circle formulas, and the various parts of a circle with a few circle practice problems on this page. A line segment with two endpoints, one on. Then, what are the radius and diameter of a circle? The set of all points on a plane that are at a fixed distance from a center. Find the area of a circle with a diameter of 10 cm. Find the area of a circle with a diameter of 10 cm. A line segment with two endpoints, one on. A few things around us that. The set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a fixed point, defined as the center, is called a circle. Circle worksheets, videos, tutorials and formulas involving arcs, chords, area, angles,. In case of a circle, it is much easier since we only need its radius or diameter to describe its geometry. A = π r 2. Let us learn more about the circle definition, the circle formulas, and the various parts of a circle with a few circle practice problems on this page. The set of all points in a. A line segment with two endpoints, one on. Find the area of a circle with a diameter of 10 cm. A circle is the set of points in a plane that are equidistant from a given point. The set of all points on a plane that are at a fixed distance from a center. The set of all points in. A circle is also termed as the locus of the points drawn at an. A line segment with two endpoints, one on. In maths or geometry, a circle is a special kind of ellipse in which the eccentricity is zero and the two foci are coincident. The circle above is called circle o. The area of a circle is π. Let us learn more about the circle definition, the circle formulas, and the various parts of a circle with a few circle practice problems on this page. The distance from the center is called the radius, and the point is called the center. The set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a fixed point, defined as. A line segment with two endpoints, one on. A = π r 2. The area of a circle is π times the radius squared, which is written: The distance from the center is called the radius, and the point is called the center. A circle is the set of points in a plane that are equidistant from a given point. The circle above is called circle o. A line segment with two endpoints, one on. Find the area of a circle with a diameter of 10 cm. Let us learn more about the circle definition, the circle formulas, and the various parts of a circle with a few circle practice problems on this page. A = π r 2. Then, what are the radius and diameter of a circle? The distance from the center is called the radius, and the point is called the center. Let us learn more about the circle definition, the circle formulas, and the various parts of a circle with a few circle practice problems on this page. The area of a circle is π. In case of a circle, it is much easier since we only need its radius or diameter to describe its geometry. The set of all points on a plane that are at a fixed distance from a center. Let us learn more about the circle definition, the circle formulas, and the various parts of a circle with a few circle. A few things around us that. Let us learn more about the circle definition, the circle formulas, and the various parts of a circle with a few circle practice problems on this page. Find the area of a circle with a diameter of 10 cm. A circle is the set of points in a plane that are equidistant from a. The set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a fixed point, defined as the center, is called a circle. Let us learn more about the circle definition, the circle formulas, and the various parts of a circle with a few circle practice problems on this page. A circle is the set of points in a plane that are equidistant from a given point. In case of a circle, it is much easier since we only need its radius or diameter to describe its geometry. The distance from the center is called the radius, and the point is called the center. Circle worksheets, videos, tutorials and formulas involving arcs, chords, area, angles, secants and more. A few things around us that. A line segment with two endpoints, one on. In maths or geometry, a circle is a special kind of ellipse in which the eccentricity is zero and the two foci are coincident. Then, what are the radius and diameter of a circle? The set of all points on a plane that are at a fixed distance from a center. Find the area of a circle with a diameter of 10 cm.Quotdna Code Circle Gene Codon Amino Acid
Printable Codon Table
Codon Chart for Biology Students
RNA Codons Chart For Amino Acids Sequences. The Codon Circle. Vector Illustratin. Stock
How To Use A Circle Codon Chart at Dominic Chumleigh blog
Circle Codon Chart
Circle codon chart.docx Google Docs
Codon Chart Table, Amino Acids & RNA Wheel Explained
Printable Codon Chart Printable Templates
Understanding A Codon Table
The Area Of A Circle Is Π Times The Radius Squared, Which Is Written:
The Circle Above Is Called Circle O.
A Circle Is Also Termed As The Locus Of The Points Drawn At An.
A = Π R 2.
Related Post: