Carburetor Adjustment Chart
Carburetor Adjustment Chart - A carburetor is a device for atomizing and vaporizing the fuel and mixing it with the air in varying proportions to suit the changing condition of spark ignition. A tube that allows air and fuel into the engine through valves, mixing them. Learn how a carburetor works. A carburetor is a key part of an engine that mixes air and fuel for the proper combustion. The carburetor sits atop the engine block beneath the air. Find out why carburetors are still used in older vehicles and how they compare to modern fuel injection systems. A carburetor takes the liquid gasoline from the gas tank and mixes it with air, which then travels to the combustion chamber, where the mixture is ignited by the spark plug. Carburetors are used to mix fuel and air together before sending the mix into the engine cylinders for ignition, powering the vehicle. A carburetor (also spelled carburettor or carburetter) [1][2][3] is a device used by a gasoline internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. A carburetor is part of an internal combustion engine that is used to mix and control the air and fuel entering the engine cylinder. Find out why carburetors are still used in older vehicles and how they compare to modern fuel injection systems. Carburetors are used to mix fuel and air together before sending the mix into the engine cylinders for ignition, powering the vehicle. A carburetor is a device for atomizing and vaporizing the fuel and mixing it with the air in varying proportions to suit the changing condition of spark ignition. Learn how a carburetor works. A carburetor takes the liquid gasoline from the gas tank and mixes it with air, which then travels to the combustion chamber, where the mixture is ignited by the spark plug. A carburetor (also spelled carburettor or carburetter) [1][2][3] is a device used by a gasoline internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. Components of carburetors typically include a chamber for. The carburetor sits atop the engine block beneath the air. A tube that allows air and fuel into the engine through valves, mixing them. A carburetor is part of an internal combustion engine that is used to mix and control the air and fuel entering the engine cylinder. Carburetors are used to mix fuel and air together before sending the mix into the engine cylinders for ignition, powering the vehicle. A tube that allows air and fuel into the engine through valves, mixing them. A carburetor is part of an internal combustion engine that is used to mix and control the air and fuel entering the engine cylinder.. A carburetor (also spelled carburettor or carburetter) [1][2][3] is a device used by a gasoline internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. A carburetor takes the liquid gasoline from the gas tank and mixes it with air, which then travels to the combustion chamber, where the mixture is ignited by the spark plug. Components. In simple words, a carburetor is a tube that sucks fuel and air. The carburetor sits atop the engine block beneath the air. A carburetor takes the liquid gasoline from the gas tank and mixes it with air, which then travels to the combustion chamber, where the mixture is ignited by the spark plug. A carburetor is a key part. In simple words, a carburetor is a tube that sucks fuel and air. A carburetor is a device for atomizing and vaporizing the fuel and mixing it with the air in varying proportions to suit the changing condition of spark ignition. Find out why carburetors are still used in older vehicles and how they compare to modern fuel injection systems.. Carburetors are used to mix fuel and air together before sending the mix into the engine cylinders for ignition, powering the vehicle. Learn how a carburetor works. A carburetor (also spelled carburettor or carburetter) [1][2][3] is a device used by a gasoline internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. A carburetor is part of. The carburetor sits atop the engine block beneath the air. A carburetor (also spelled carburettor or carburetter) [1][2][3] is a device used by a gasoline internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. A carburetor is a device for atomizing and vaporizing the fuel and mixing it with the air in varying proportions to suit. In simple words, a carburetor is a tube that sucks fuel and air. Carburetors are used to mix fuel and air together before sending the mix into the engine cylinders for ignition, powering the vehicle. The carburetor sits atop the engine block beneath the air. A carburetor takes the liquid gasoline from the gas tank and mixes it with air,. Carburetors are used to mix fuel and air together before sending the mix into the engine cylinders for ignition, powering the vehicle. A carburetor is a device for atomizing and vaporizing the fuel and mixing it with the air in varying proportions to suit the changing condition of spark ignition. In simple words, a carburetor is a tube that sucks. Carburetors are used to mix fuel and air together before sending the mix into the engine cylinders for ignition, powering the vehicle. Components of carburetors typically include a chamber for. A carburetor (also spelled carburettor or carburetter) [1][2][3] is a device used by a gasoline internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. A carburetor. Find out why carburetors are still used in older vehicles and how they compare to modern fuel injection systems. Carburetors are used to mix fuel and air together before sending the mix into the engine cylinders for ignition, powering the vehicle. Components of carburetors typically include a chamber for. A carburetor (also spelled carburettor or carburetter) [1][2][3] is a device. A carburetor is a key part of an engine that mixes air and fuel for the proper combustion. Find out why carburetors are still used in older vehicles and how they compare to modern fuel injection systems. Carburetors are used to mix fuel and air together before sending the mix into the engine cylinders for ignition, powering the vehicle. In simple words, a carburetor is a tube that sucks fuel and air. The carburetor sits atop the engine block beneath the air. A carburetor is part of an internal combustion engine that is used to mix and control the air and fuel entering the engine cylinder. Components of carburetors typically include a chamber for. A carburetor takes the liquid gasoline from the gas tank and mixes it with air, which then travels to the combustion chamber, where the mixture is ignited by the spark plug. A carburetor is a device for atomizing and vaporizing the fuel and mixing it with the air in varying proportions to suit the changing condition of spark ignition.How to Adjust a Carburetor and When Is Tuning Needed? In The Garage with
Basic Carburetor Adjustment & Tips A Guide To Tuning A Carburetor JEGS
How to Tune and Adjust Your Carburetor YourMechanic Advice
Carburetor Tuning Quick Reference ProCycle.us
Repair Guides Carbureted Fuel System Carburetor
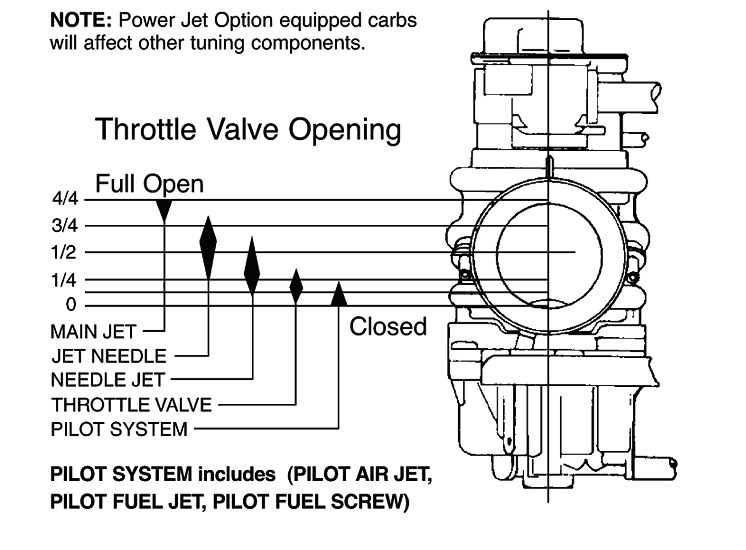
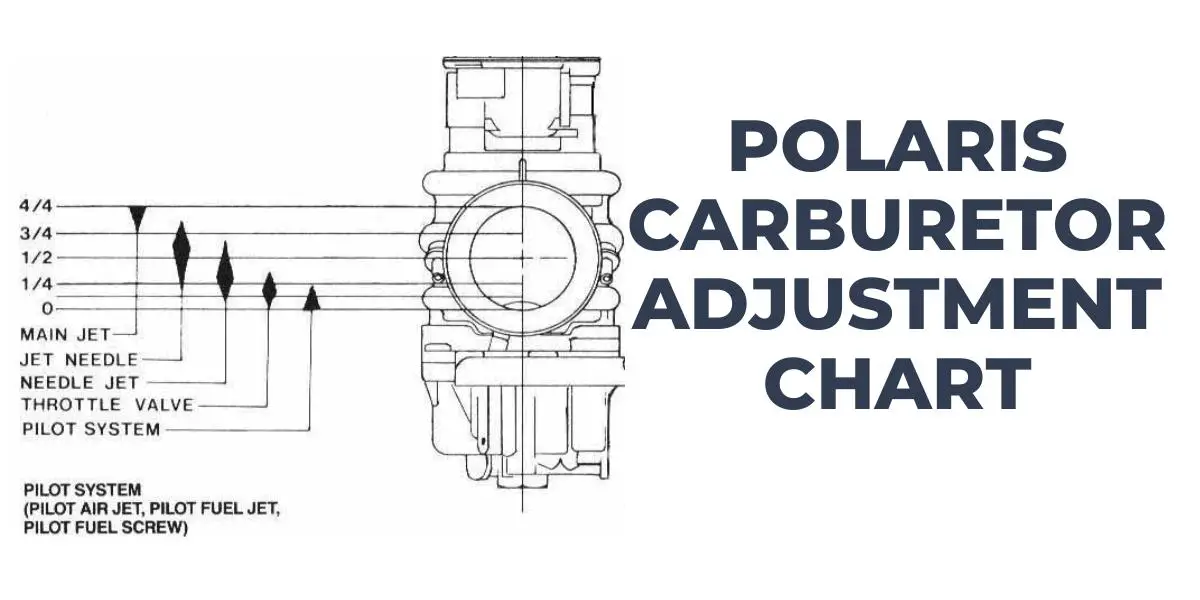
Polaris Carburetor Adjustment Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
Adjustment Mikuni Carb Adjustment
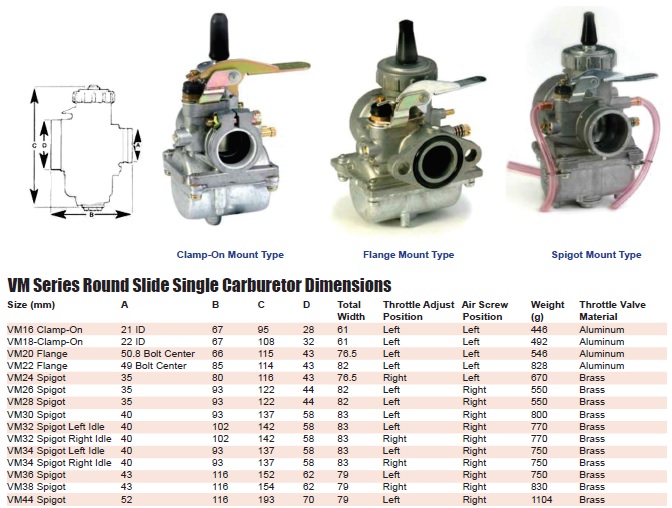
Mikuni Carburetor Identification Chart
Polaris Carburetor Adjustment Chart & How to Adjust (Guide)
Basics Of A Carburetor at Kristina Hertz blog
Learn How A Carburetor Works.
A Tube That Allows Air And Fuel Into The Engine Through Valves, Mixing Them.
A Carburetor (Also Spelled Carburettor Or Carburetter) [1][2][3] Is A Device Used By A Gasoline Internal Combustion Engine To Control And Mix Air And Fuel Entering The Engine.
Related Post: